A mismatch tolerance test assay, based on pools of transgenic strains, revealed that target hybridization to nucleotides of the seed region, at the 5′ end of an miRNA, was sufficient to induce moderate repression of expression In contrast, pairing to the 3′ region of the miRNA was not critical for silencing Furthermore, we evaluated the silencing efficiencies of miRNAs with the same seven nucleotide compositions in their seed regions (A = 3, U =The latest version of this resource was released in August 15 miRSearch

Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Sciencedirect
Seed region of mirna
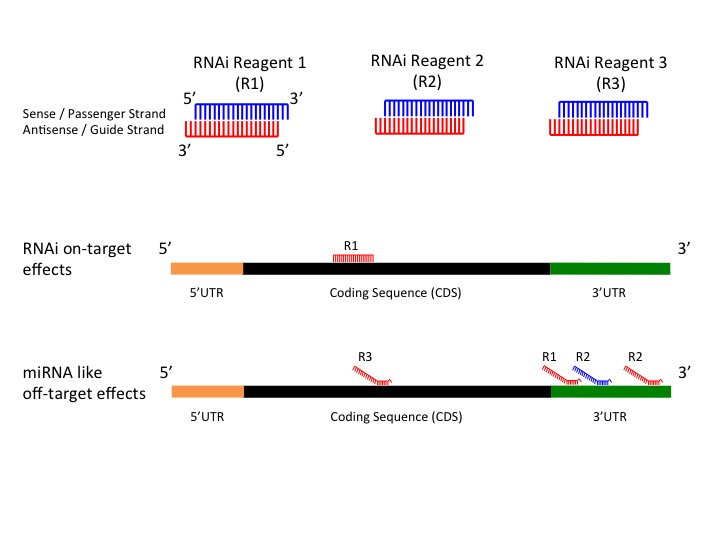
Seed region of mirna-MiRNA seed region is more critical than the 3′ region for target recognition in A thaliana (Mallory et al, 04) Moreover, plant and algal small RNAs also induce translational repression of perfectly complementary target mRNAs without, or with only minimal, transcript destabiliOnline GESS prediction of miRNAlike offtarget effects in largescale RNAi screen data by seed region analysis Bahar Yilmazel1, Yanhui Hu1, Frederic Sigoillot2, Jennifer A Smith3, Caroline E Shamu3, Norbert Perrimon1,4 and Stephanie E Mohr1* Abstract Background RNA interference (RNAi) is an effective and important tool used to study gene




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science
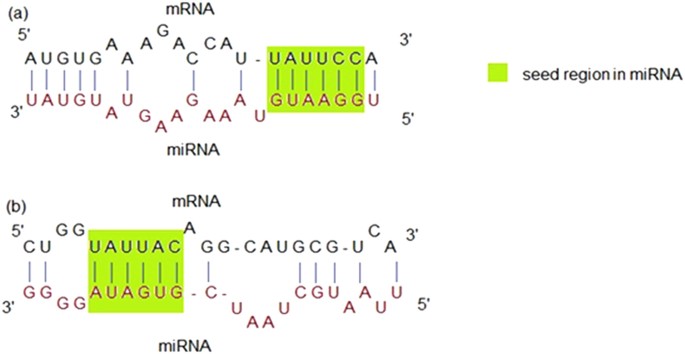
The most critical region for complementarity is the seed region (nucleotides 2–7 from the 5'terminus of the miRNA) 4,7 Aside from the seed region, other criteria have been established that can enhance miRNAmediated repression including complementarity at position 8 and the presence of an adenosine residue opposite the first miRNAMicroRNA Editing in Seed Region Aligns With Cellular Changes in Hypoxic Conditions PubMed RNA editing is a finely tuned, dynamic mechanism for posttranscriptional gene regulation that has been thoroughly investigated in the last decadeReveal that miRNA containing inosine in the seed region exhibits a different degree of silencing efficiency compared to the corresponding miRNA with guanosine at the same position The difference in basepairing stability, deduced by melting temperature measurements, between seedtarget duplexes containing either CG or IC pairs may account for
This mature miRNA SNP (miRSNP) is located within the "seed region";To avoid miRNAlike offtarget effect, the logical approach is to reduce complementarity between the seed region (2–7 nucleotides of 5′ end) of siRNA and the 3′UTR of mRNA Clearly, the seed sequences of miRNA (identified with miRNA databases) should be avoided in siRNA designTargetScan predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of 8mer, 7mer, and 6mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA As an option, only conserved sites are predicted Also identified are sites with mismatches in the seed region that are compensated by conserved 3' pairing and centered sites
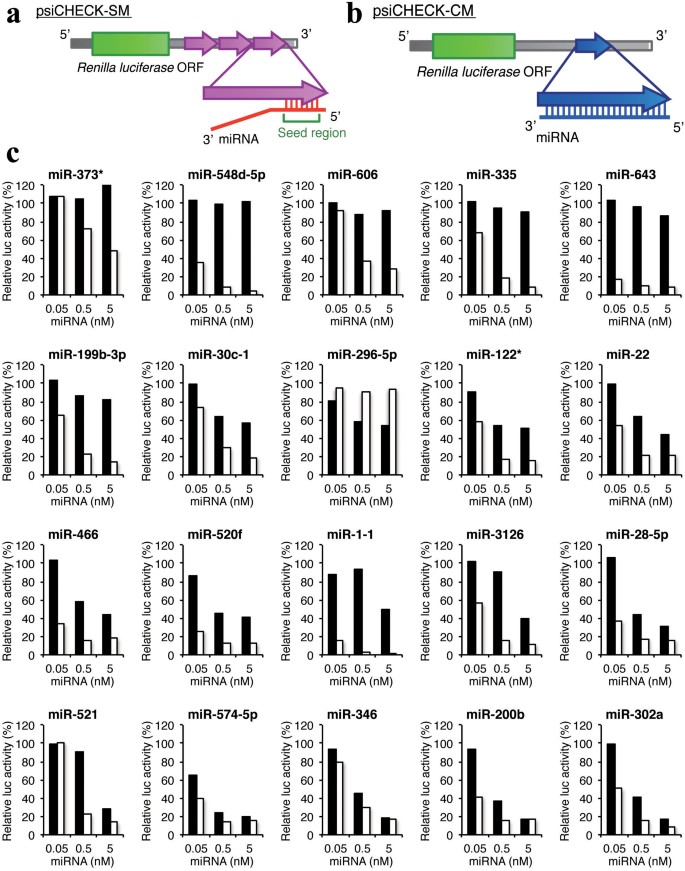
The impact of miRNA seed types on target downregulation Previous studies have identified several major types of canonical miRNA target sites, including those matching to the 6mer, 7mer, or 8mer miRNA seed sequences (Table 2)Sequence conservation analysis suggested that target sites pairing to longer miRNA seeds are more conserved across species and thus are Results from luciferasereporter assays and global expression data confirmed previous observations that the siRNA seed region is the primary determinant for offtarget gene recognition and binding To characterize the basepairing patterns of miRNAtarget interaction, we searched for overrepresented sequence elements in all the targets discovered for each miRNA For most of the top expressed miRNAs, highly enriched sequence motifs emerged as complementary to the extended miRNA seed region (nucleotides 1–8 of miRNA) (Fig 4A and S7 Fig)




Helix 7 In Argonaute2 Shapes The Microrna Seed Region For Rapid Target Recognition The Embo Journal



Miraw A Deep Learning Based Approach To Predict Microrna Targets By Analyzing Whole Microrna Transcripts
One class of pattern consists of perfect WatsonCrick binding at the 5'end of the miRNA This region is known as "seedregion" and found at the 27 base of the miRNA This region is able to suppress the target mRNAs without having a complete base pairing atThe seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed sequence" has to be perfectly complementaryTargetScan is a target prediciton tool that predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of conserved 8mer and 7mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA The target prediction software is frequently updated;



Gess



Mirepress Modelling Gene Expression Regulation By Microrna With Non Conventional Binding Sites Scientific Reports
Specifically, seedbased canonical target recognition was dependent on the GC content of the miRNA seed For miRNAs with low GC content of the seed region, noncanonical targeting was the dominant mechanism for target recognition In contrast to canonical targeting, noncanonical targeting did not lead to significant target downregulation at MicroRNAs (miRNAs) bind to mRNAs and target them for translational inhibition or transcriptional degradation It is thought that most miRNAmRNA interactions involve the seed region at the 5′ end of the miRNA The importance of seed sites is supported by experimental evidence, although there is growing interest in interactions mediated by the central region of the miRNABasepairing of the socalled miRNA "seed" region with mRNAs identifies many thousands of putative targets Evaluating the strength of the resulting mRNA repression remains challenging, but is essential for a biologically informative ranking of potential miRNA targets




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science
After the siRNA seed region anneals, the catalytic RNase H domain of Argonaute then subjects perfectly complementary mRNA sequences 10 nucleotides from the 5' end of the incorporated siRNA strand to nucleolytic degradation, resulting inFor the 1226 human miRNAs with SNPs in their seed region, 314 (256%) of them are located in miRNA clusters, whereas among the 1587 human miRNAs without SNPs in their seed region, only 3 (2%) of them are located in miRNA clusters (P = 606 × 10 −4, χ 2 test) (Table S2) miRNAs from the same cluster have the tendency to regulate theSOFTWARE Open Access Online GESS prediction of miRNAlike offtarget effects in largescale RNAi screen data by seed region analysis Bahar Yilmazel1, Yanhui Hu1, Frederic Sigoillot2, Jennifer A Smith3, Caroline E Shamu3, Norbert Perrimon1,4 and Stephanie E Mohr1* Abstract



Microrna Wikipedia



Multimitar A Novel Multi Objective Optimization Based Mirna Target Prediction Method
Defined as six or seven nucleotides between the nucleotides 27 or 28 of the miRNA 5' end that are responsible for mRNA binding 11(Figure (Figure11C)TargetScan predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of conserved 8mer, 7mer, and 6mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA (Lewis et al, 05)As an option, predictions with only poorly conserved sites are also providedAtoI editing in the miRNA seed region regulates target mRNA selection and silencing efficiency 11 Pages AtoI editing in the miRNA seed region regulates target mRNA selection and silencing efficiency Nucleic acids research, 14 Josephine Galipon Download PDF




Rna Targeting Utilizing Pairing Outside Of The Canonical Mirna 5 Seed Download Scientific Diagram
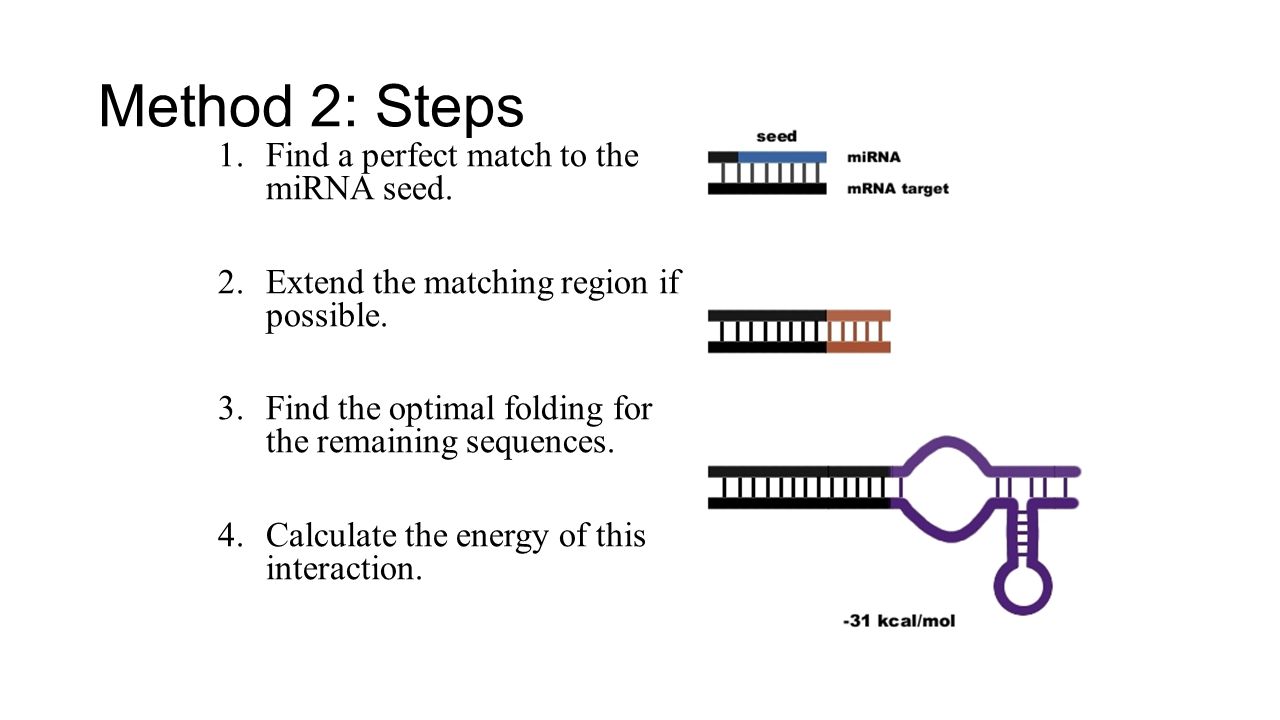



Microrna Computational Prediction And Analysis Ppt Download
Part of a miRNA is a 2–8base pair long seed region in their 5′ end The interaction happens between these seed regions and complementary "seed matches" on the target sites of the mRNAs 7A mismatch tolerance test assay, based on pools of transgenic strains, revealed that target hybridization to nucleotides of the seed region, at the 5′ end of an miRNA, was sufficient to induce moderate repression of expression In contrast, pairingIn molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codonThe 3′UTR often contains regulatory regions that posttranscriptionally influence gene expression During gene expression, an mRNA molecule is transcribed from the DNA sequence and is later translated into a protein



Plos One Evolution Of Microrna In Primates




Snps In Microrna Target Sites And Their Potential Role In Human Disease Open Biology
Editing in microRNAs, particularly in seed can significantly alter the choice of their target genes We show that out of 13 different human tissues, different regions of brain sho Our results demonstrate that SNPs in clustered miRNA seed regions can take part in more intricate generegulating networks with lower functional cost by functional complementarity 2 Materials and Methods 21 GenomeWide Identification of SNPs in Human miRNA Seed RegionsThe seed regions are regions present within the miRNA binding regions Although there are several factors that pave a way to the binding between miRNA and mRNA, the impact of binding is determined by the seed sequence within the miRNA The seed region consists of a continuous string of at least 6 to 8 nucleotides miRNA recognizes its target by




Microrna Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms And Diabetes Mellitus A Comprehensive Review Zhang 19 Clinical Genetics Wiley Online Library




Target Recognition By Sirna And Mirna A Sirna Is Usually Fully Download Scientific Diagram
TargetScan predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of conserved 8mer, 7mer, and 6mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA (Lewis et al, 05)As an option, predictions with only poorly conserved sites are also provided Seed Pairing Is Enriched in miRNATarget Sites The miRNA sequence can be separated into five functional domains that affect miRNAtarget recognition 5′ anchor (nt 1), seed sequence (nts 2–8), central region (nts 9–12), 3′ supplementary region (nts 13–16), and 3′ tail (nts 17–22) (Wee et al, 12)And some miRNA nucleotides are more important than others (8, 9) Specifically, pairing to the miRNA "seed region" (nt 2 to 7 or 2 to 8, from the 5′ end) is the most evolutionarily conserved feature of miRNA targets in animals (10–14) Crystal structures of human Argonaute proteins show nt 2 to 6 of the guide RNA bound
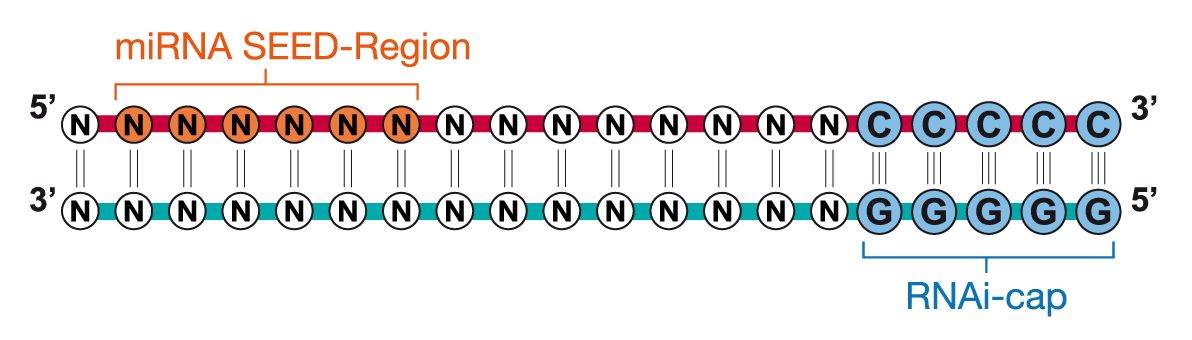



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna
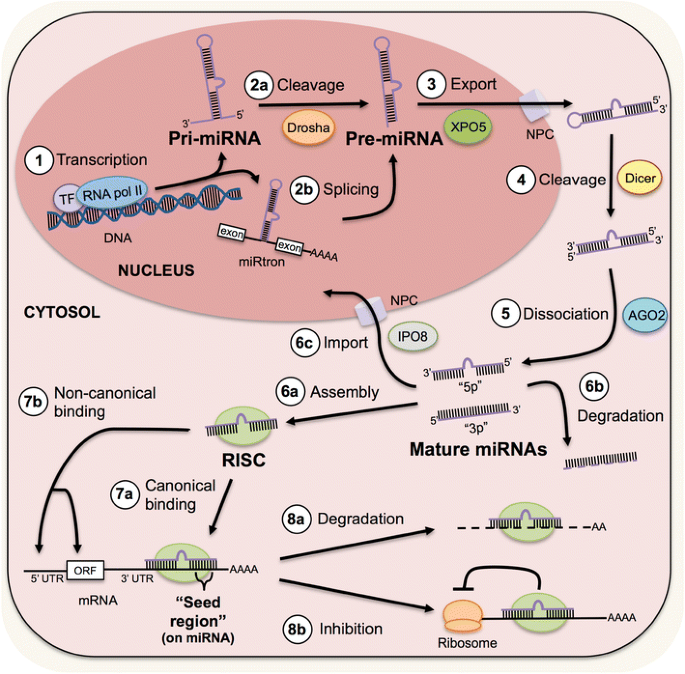



Micrornas In Injury And Repair Springerlink
In human miRNA seed regions A total of 1879 SNPs were mapped to 1226 human miRNA seed regions We found that miRNAs with SNPs in their seed region are significantly enriched in miRNA clusters We also found that SNPs in clustered miRNA seed regions have a lower functional effect than have SNPs in nonclustered miRNA seed regions Additionally, we Further studies revealed that the pairing of miRNA position 8 was dispensable in many cases, indicating that the seed region can be asCanonically, miRNA targeting is reliant on base pairing of the seed region, nucleotides 2–7, of the miRNA to sites in mRNA 3′ untranslated regions Recently, the 3′ half of the miRNA has gained attention for newly appreciated roles in regulating target specificity and regulation
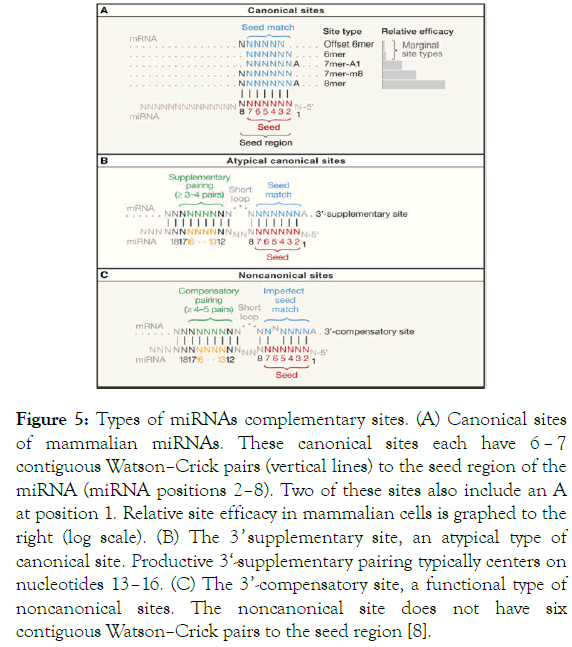



Micrornas In Skin Biology Biogenesis Regulations And Functions In Homeostasis And Diseases




Structural Differences Between Pri Mirna Paralogs Promote Alternative Drosha Cleavage And Expand Target Repertoires Sciencedirect
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key regulators of sequencespecific gene silencing However, crucial factors that determine the efficacy of miRNAmediated target gene silencing are poorly understood Here we mathematized basepairing stability and showed that miRNAs with an unstable 5′ terminal duplex and stable seedtarget duplex exhibit strong silencing activityMouse let7 miRNA populations exhibit RNA editing that is constrained in the 5'seed/ cleavage/anchor regions and stabilize predicted mmulet7amRNA duplexes 11SCIENTIFIC REPORTS srep 1 wwwnaturecomscientificreports Long noncoding RNAs harboring miRNA seed regions are enriched in prostate cancer exosomes Alireza Ahadi1,2, Samuel Brennan3, Paul J Kennedy2,4, Gyorgy Hutvagner2 & Nham Tran2,5 Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) form the largest transcript class in the human transcriptome




Systematic Prediction Of The Impacts Of Mutations In Microrna Seed Sequences




Mechanisms Of Action Of Micrornas A Mirnas Bind The 3 Utr Of A Target Download Scientific Diagram
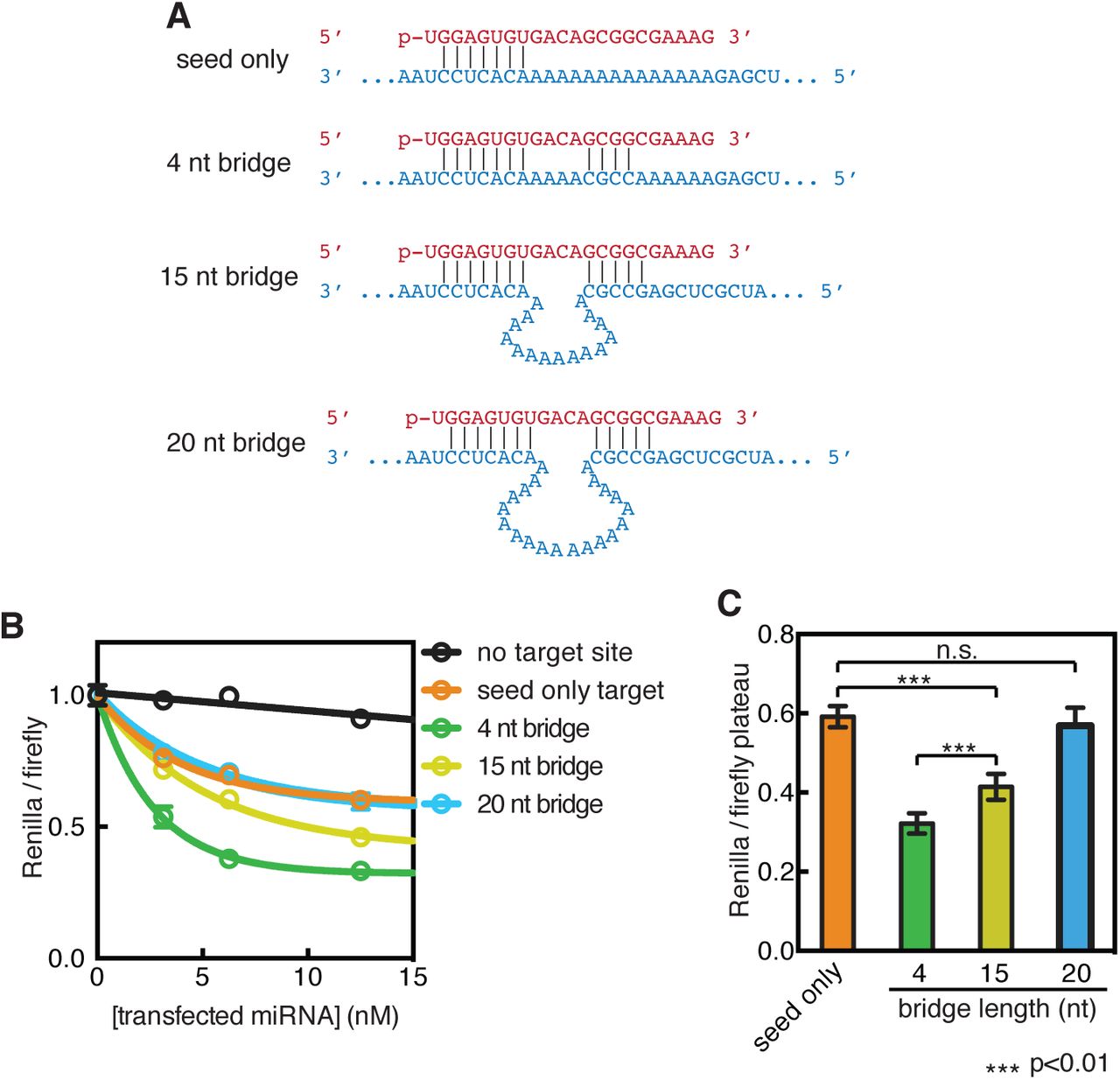
I microRNA si appaiano all'mRNA target attraverso i nucleotidi 28 del miRNA (seed region) e il sito complementare della regione 3'UTR dell'mRNA bersaglio PDF PDFComplementarity to an miRNA Seed Region Is Sufficient to Induce Moderate Repression of a Target Transcript in the Unicellular Green Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Tomohito Yamasaki,1 Adam Voshall,2 EunJeong Kim,2 Etsuko Moriyama,2 Heriberto Cerutti,2 and Takeshi Ohama1 1
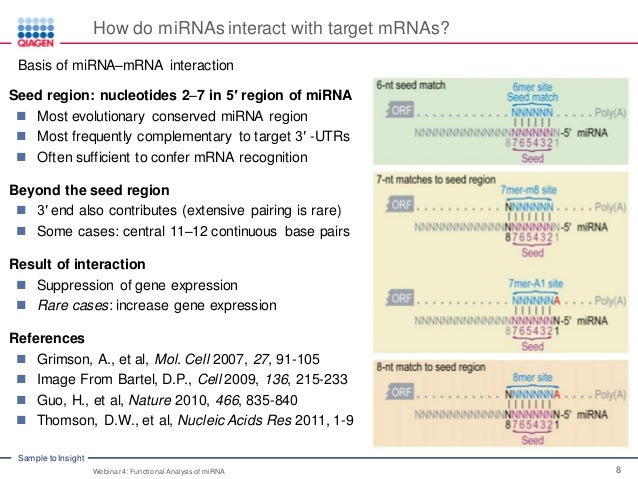



Ynupjjdamdxssm




Three Classes Of Mirna Target Sites Model Of Canonical Left Seed Download Scientific Diagram



Plos One Micrornas Mir 19 Mir 340 Mir 374 And Mir 542 Regulate Mid1 Protein Expression
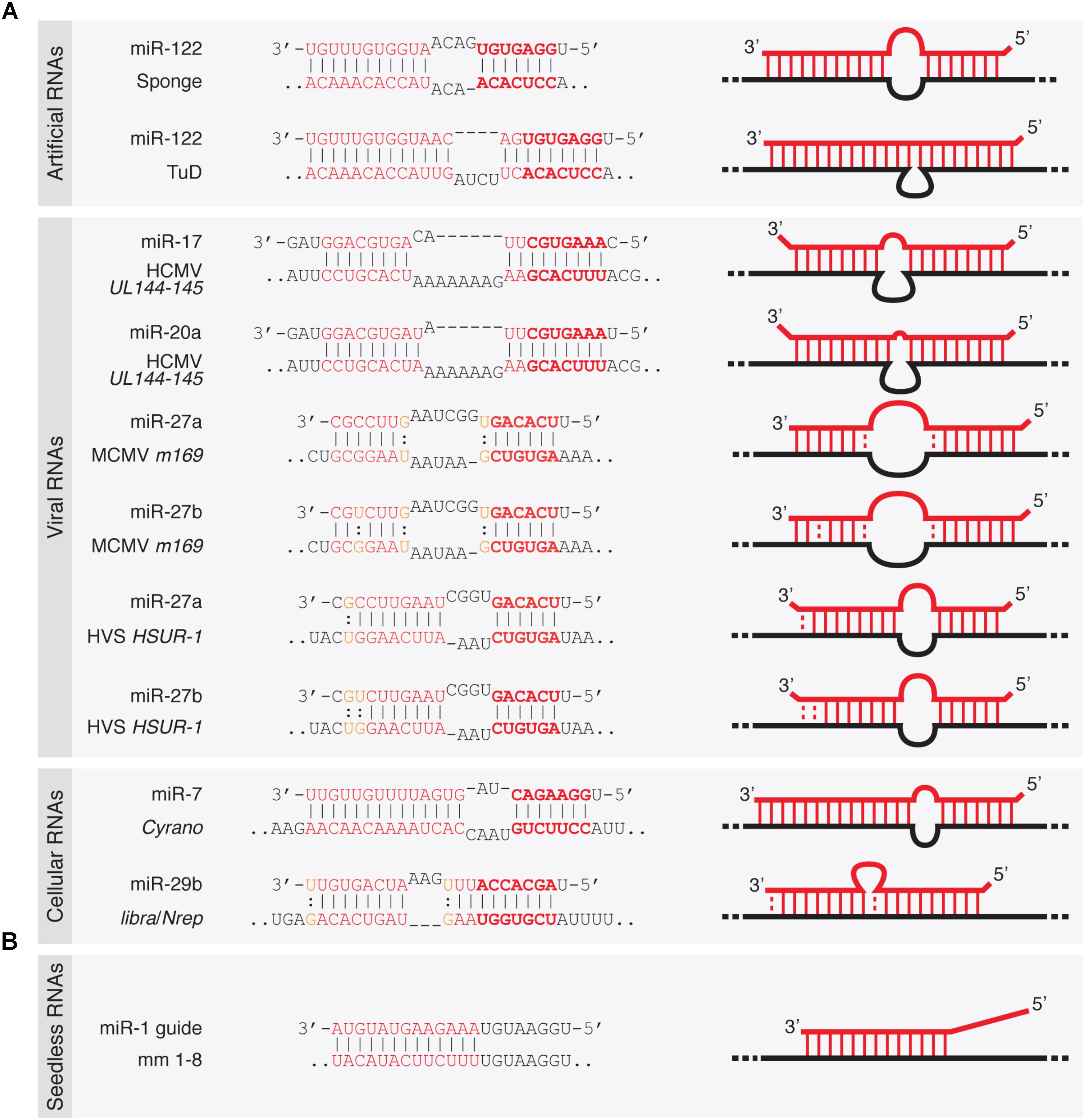



Frontiers Target Rnas Strike Back On Micrornas Genetics




Mismatches In The Mirna Proximal Seed Region Disrupt The Binding Download Scientific Diagram
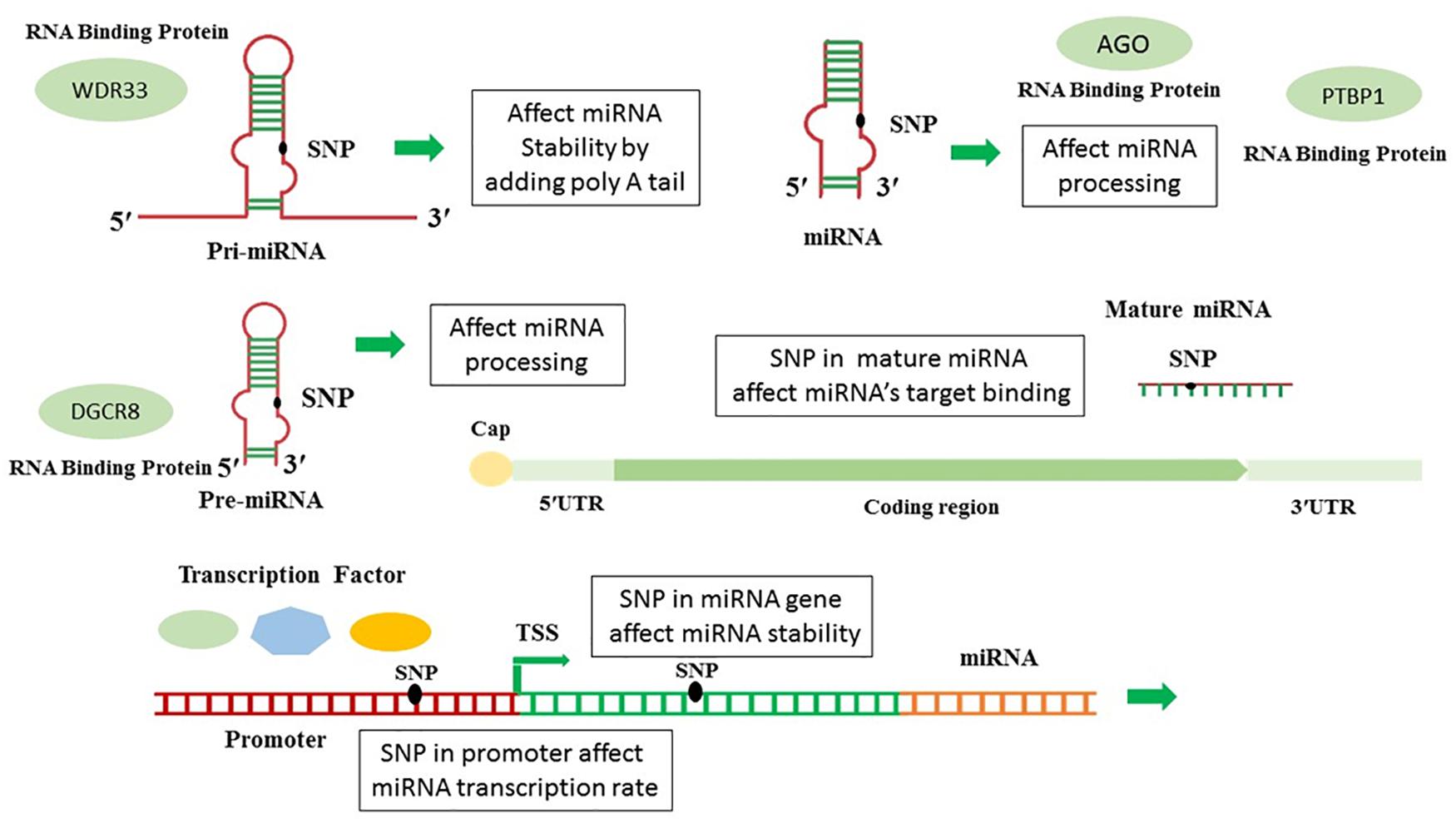



Frontiers In Silico Analysis Of Polymorphisms In Micrornas Deregulated In Alzheimer Disease Neuroscience




A Simplified System To Express Circularized Inhibitors Of Mirna For Stable And Potent Suppression Of Mirna Functions Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids




A Cartoon Showing The Site And Mechanism Of Mirna Targeting To Mrna Download Scientific Diagram
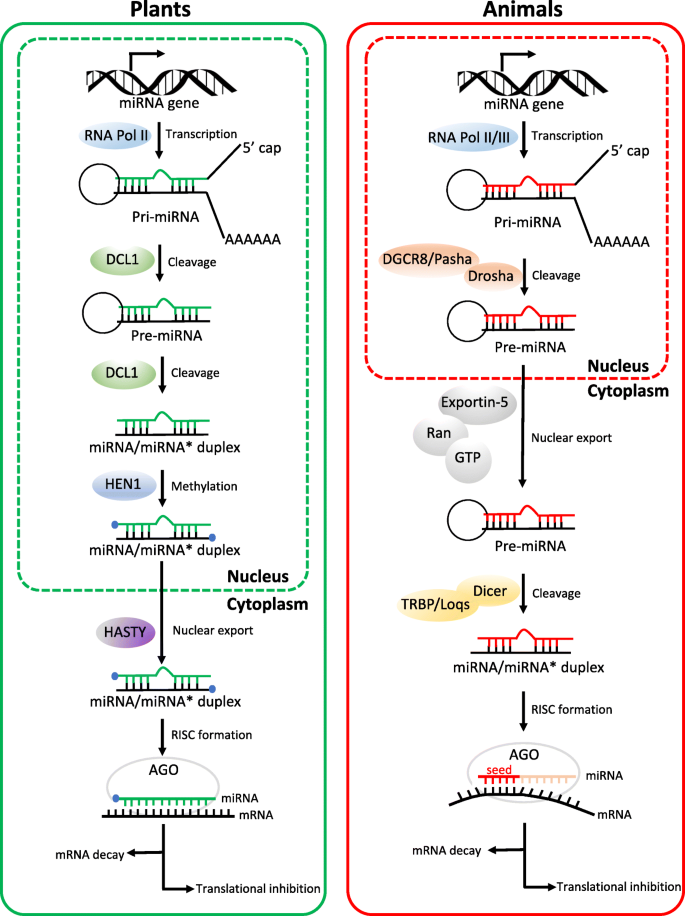



Micrornas From Plants To Animals Do They Define A New Messenger For Communication Nutrition Metabolism Full Text




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal




Mirna Seed Types Nine Seed Types Are Categorized In Two Groups Download Scientific Diagram
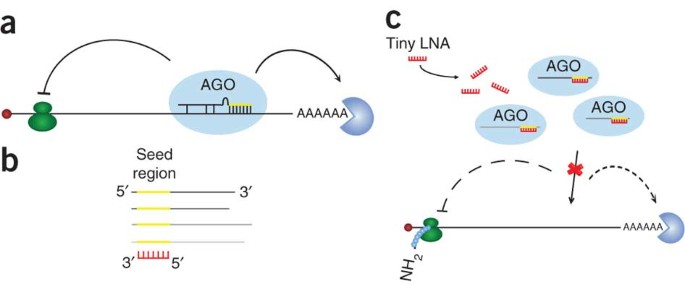



Silencing Of Microrna Families By Seed Targeting Tiny Lnas Nature Genetics




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal
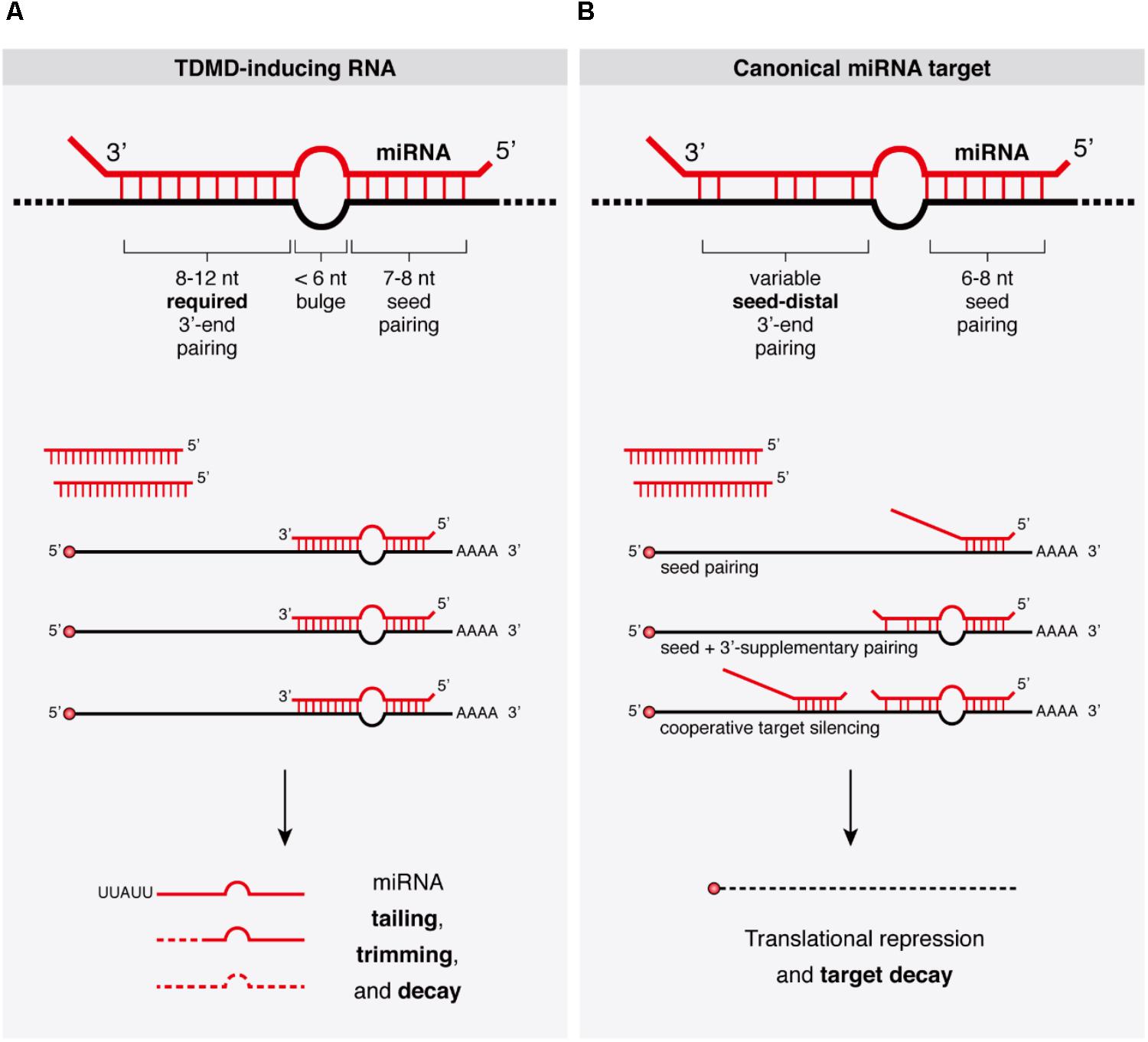



Frontiers Target Rnas Strike Back On Micrornas Genetics




A Study Of Micrornas In Silico And In Vivo Bioimaging Of Microrna Biogenesis And Regulation Kim 09 The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library
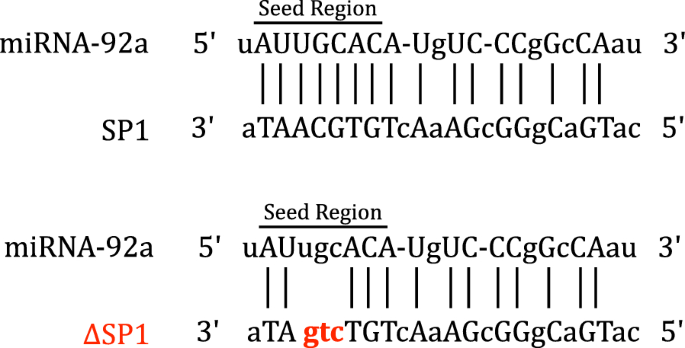



Microrna 92a Regulates The Expression Of Aphid Bacteriocyte Specific Secreted Protein 1 Bmc Research Notes Full Text
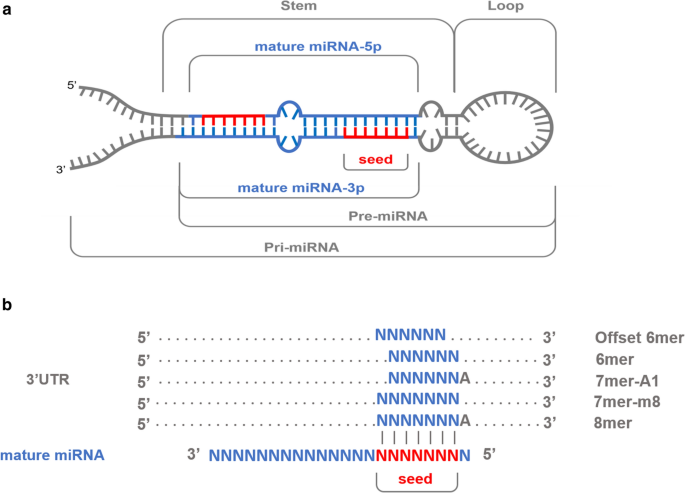



Variability In Porcine Microrna Genes And Its Association With Mrna Expression And Lipid Phenotypes Genetics Selection Evolution Full Text




An Overview Of The Mirna Processing Pathway And Mechanism Of Mirna Download Scientific Diagram




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal




Sites Matching In The Mirna Seed Region Including All K Mer 8mer Download Scientific Diagram




Human Polymorphism At Micrornas And Microrna Target Sites Pnas



Upcommons Upc Edu Bitstream Handle 2117 Pdf Sequence 1 Isallowed Y




Microrna Wikipedia




Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Cell
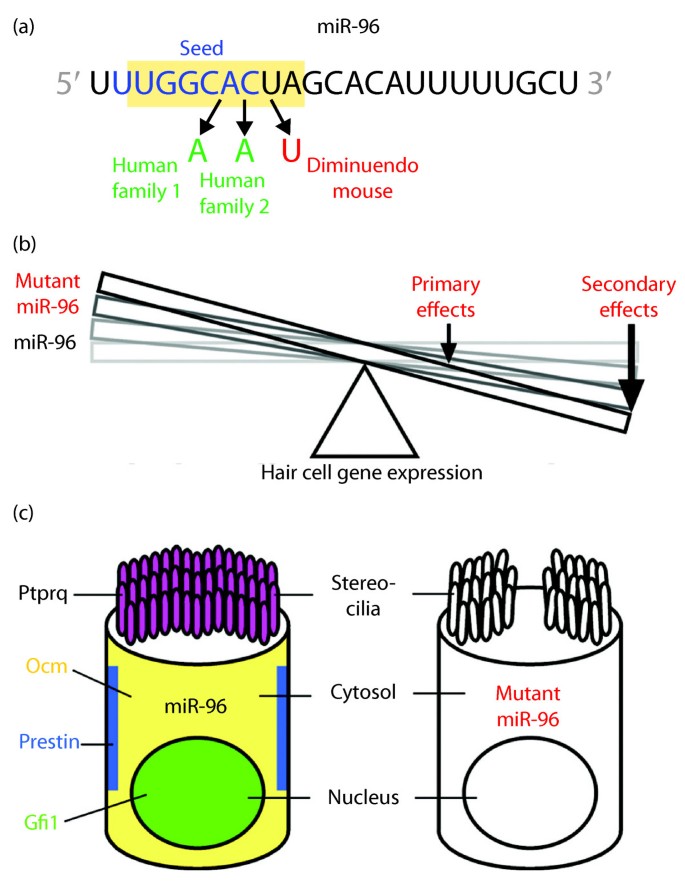



Micrornas Sound Off Genome Medicine Full Text




Pairing Beyond The Seed Supports Microrna Targeting Specificity Sciencedirect




Dbmts A Comprehensive Database Of Putative Human Microrna Target Site Snvs And Their Functional Predictions Li Human Mutation Wiley Online Library




Mirna 27b Targets The 3 Utr Of Foxj3 A Sequence Alignment Of Download Scientific Diagram




Mirna Binding Sequences In The Serpine1 3 9 Utr Region The 3 9 Utr Download Scientific Diagram
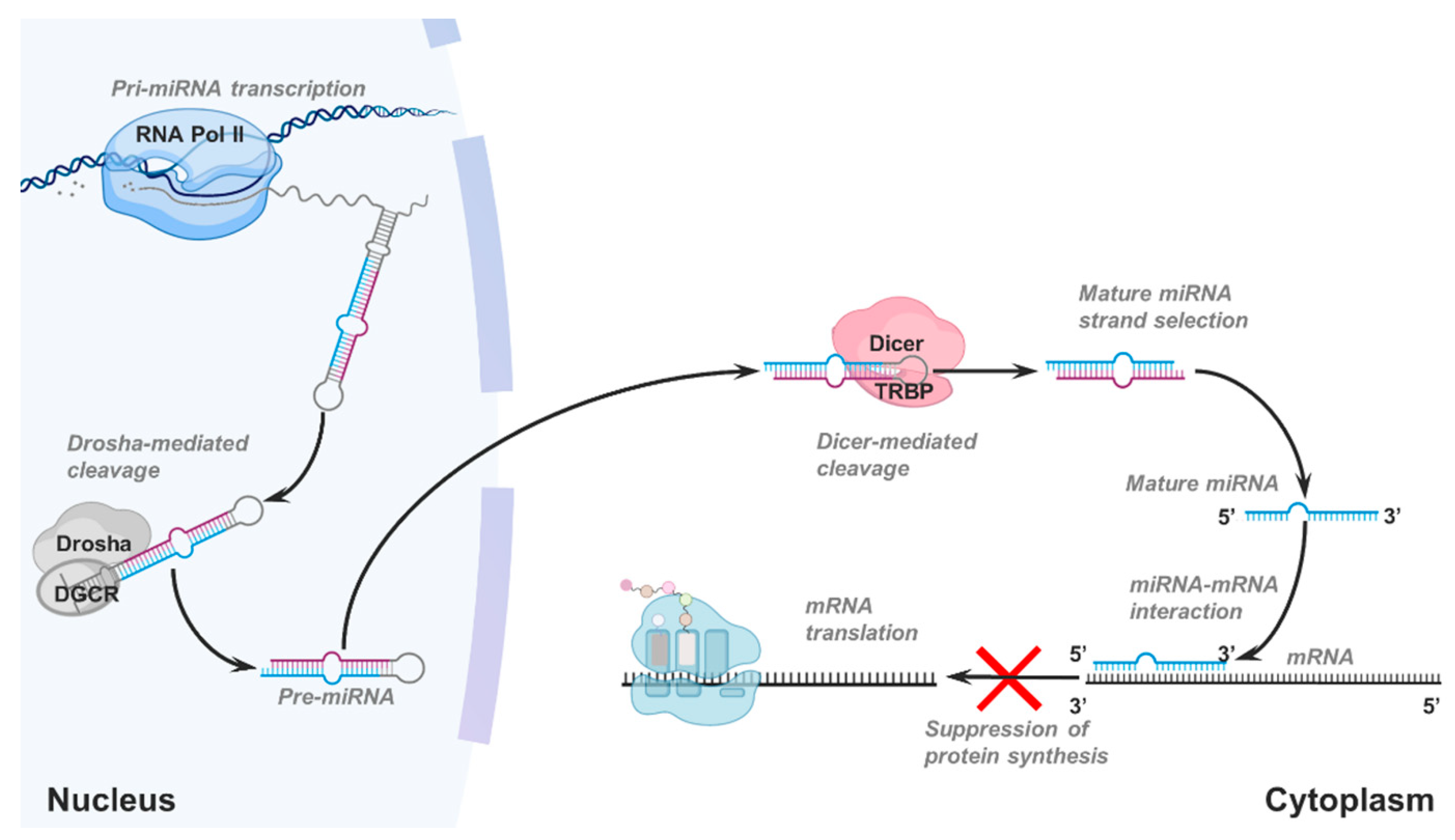



Cancers Free Full Text Detecting And Characterizing A To I Microrna Editing In Cancer Html



1



1
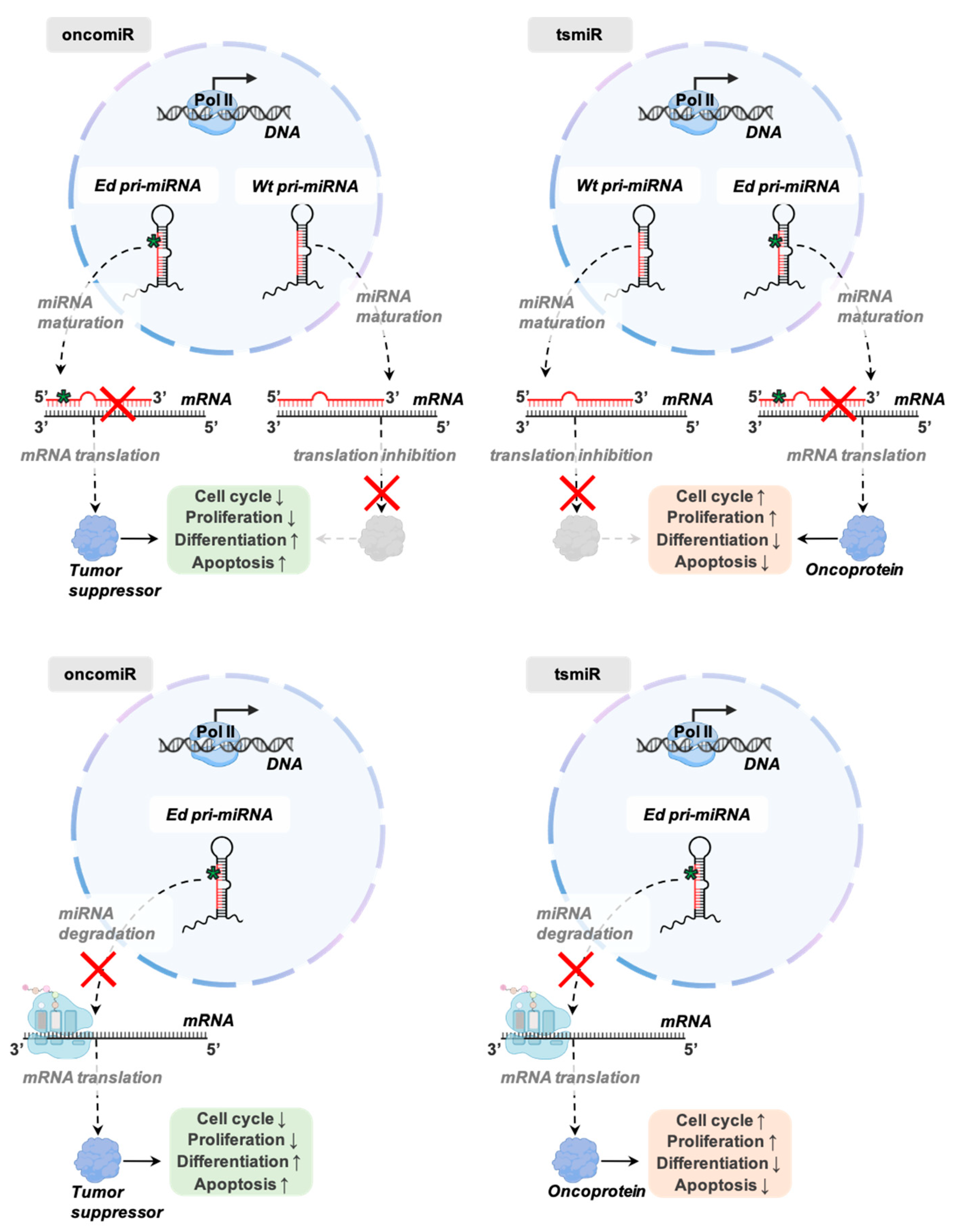



Cancers Free Full Text Detecting And Characterizing A To I Microrna Editing In Cancer Html




Opportunities And Challenges For Microrna Targeting Therapeutics For Epilepsy Sciencedirect
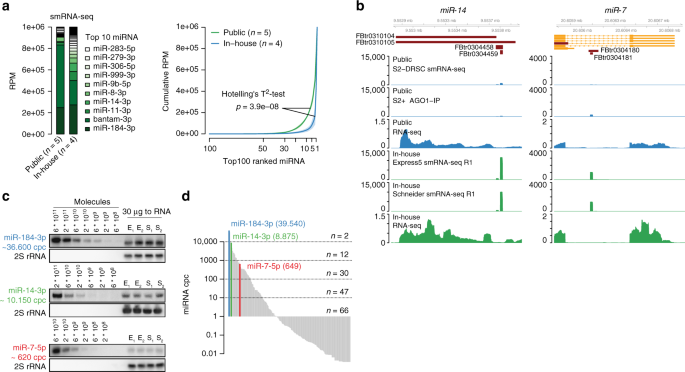



Global Identification Of Functional Microrna Mrna Interactions In Drosophila Nature Communications




Metazoan Micrornas Sciencedirect



Www Cell Com Cell Pdf S0092 8674 18 1 Pdf




Types Of Mirna Target Sites And Multiple Sites A Stringent Seed Download Scientific Diagram
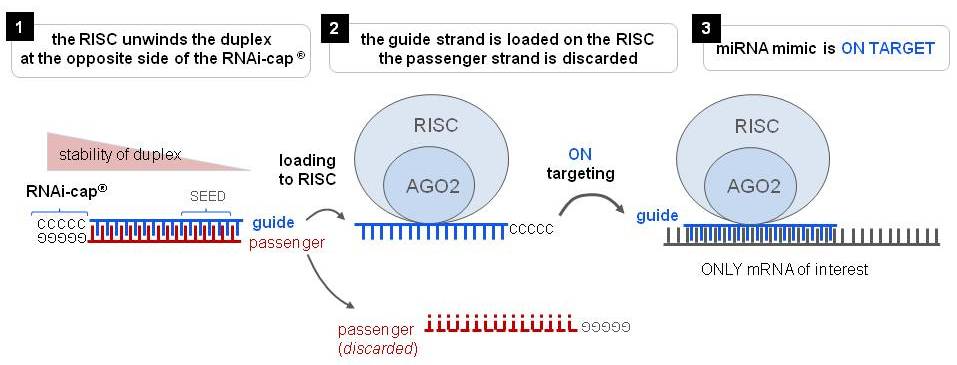



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna




Microrna Regulation And Cardiac Calcium Signaling Circulation Research




Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Sciencedirect
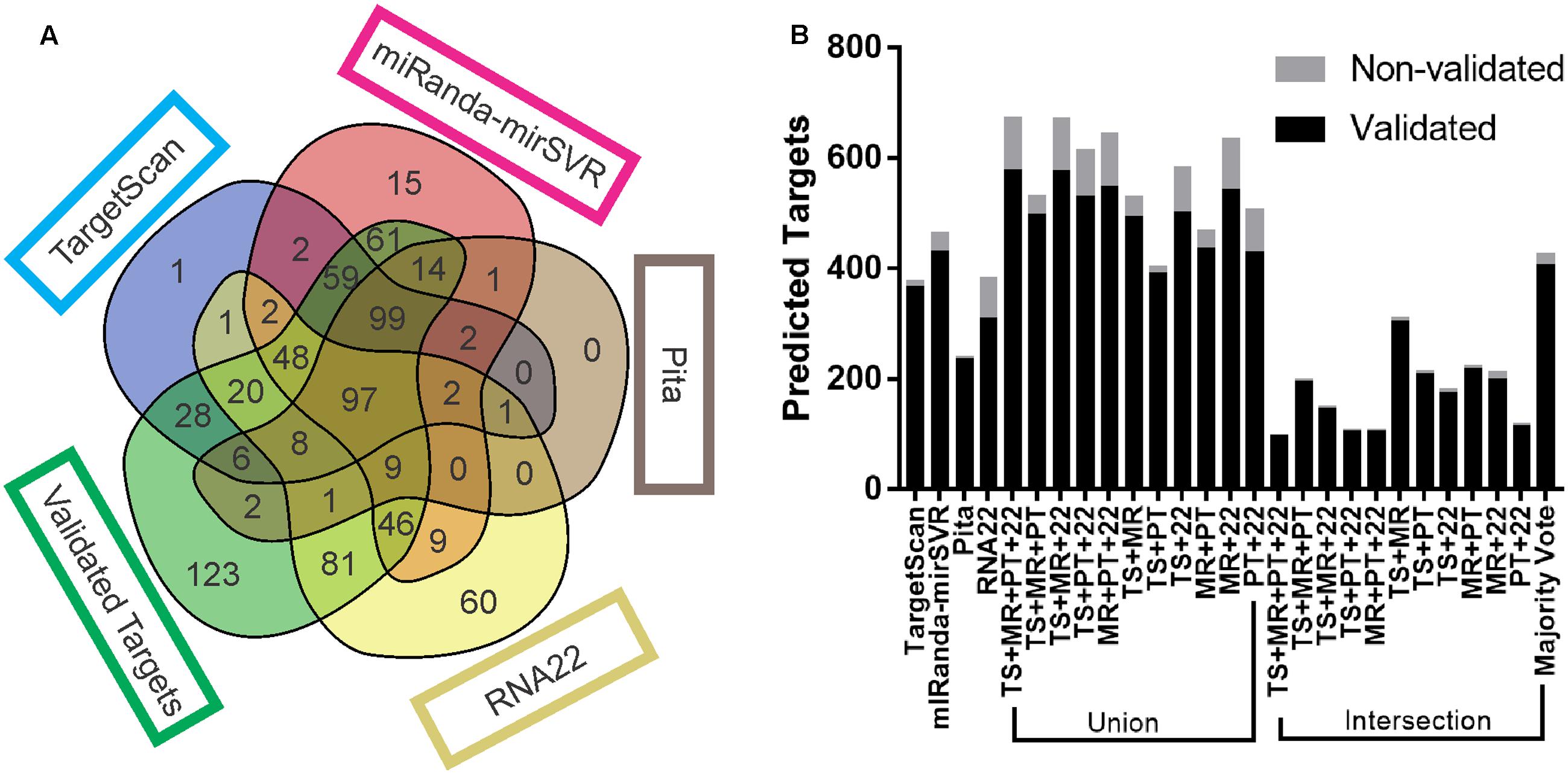



Frontiers Combining Results From Distinct Microrna Target Prediction Tools Enhances The Performance Of Analyses Genetics




Helix 7 In Argonaute2 Shapes The Microrna Seed Region For Rapid Target Recognition The Embo Journal




Mirna Introduction Biogenesis Nomenclature And Experimental Workflow
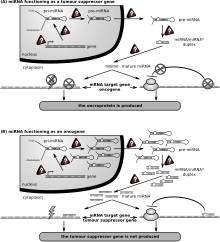



Microrna Wikipedia




Chemical Modifications In The Seed Region Of Mirnas 221 222 Increase The Silencing Performances In Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Cells Sciencedirect




Crispr Screening Strategies For Microrna Target Identification Yang The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library
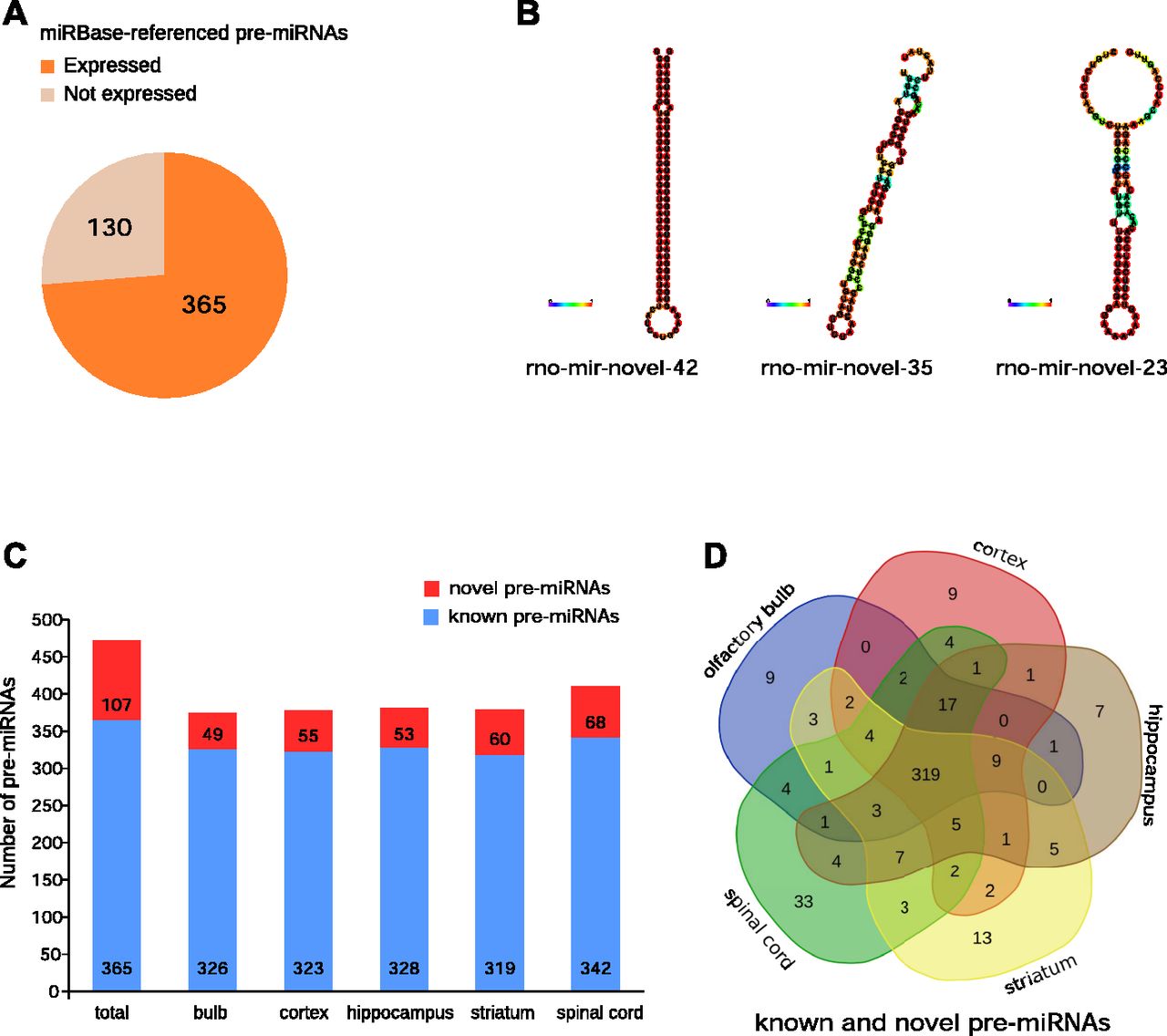



Small Rna Seq Reveals Novel Mirnas Shaping The Transcriptomic Identity Of Rat Brain Structures Life Science Alliance




Examples Of Mirna Target Interactions Pairing Schemes Of Several Download Scientific Diagram
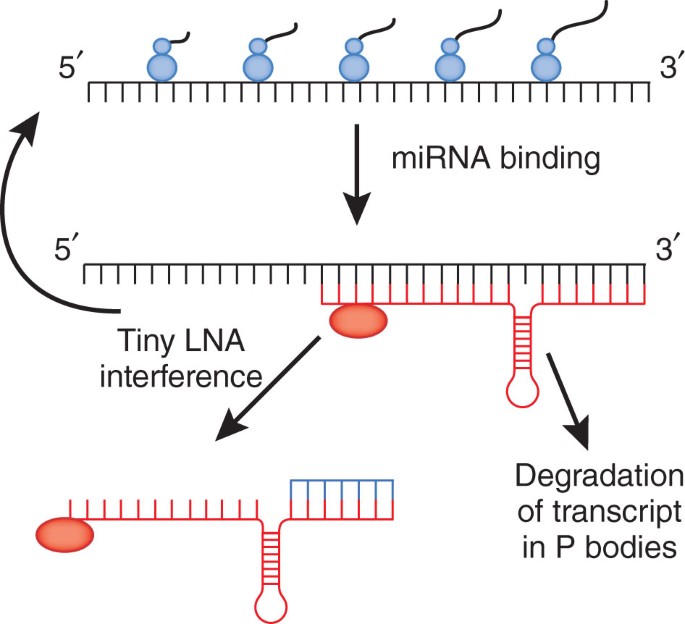



Stopping Rna Interference At The Seed Nature Genetics




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Biorxiv




The Characterization Of Microrna Mediated Gene Regulation As Impacted By Both Target Site Location And Seed Match Type




Tiny Giants Of Gene Regulation Experimental Strategies For Microrna Functional Studies Steinkraus 16 Wires Developmental Biology Wiley Online Library




Mirbase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
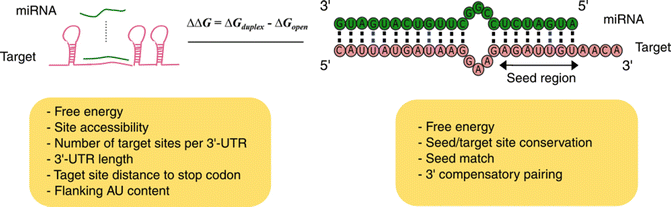



Computational And Experimental Identification Of Tissue Specific Microrna Targets Springerlink




Different Seed Match Regions Of Mirnas Mirnalyze Follows A Download Scientific Diagram




Micrornas Modulate Alternative Splicing In The C Elegans Intestine And Body Muscle Tissues Biorxiv



1




Dbmts A Comprehensive Database Of Putative Human Microrna Target Site Snvs And Their Functional Predictions Li Human Mutation Wiley Online Library




Rna Mrna Target Interaction Schematic Overview Of A Mirna Interaction Download Scientific Diagram




Pairing Beyond The Seed Supports Microrna Targeting Specificity Sciencedirect




Design Of Artificial Mirnas With Seed Matches To Multiple Target Genes Download Scientific Diagram



New Insights Into The Function Of Mammalian Argonaute2




Microrna Polymorphisms The Future Of Pharmacogenomics Molecular Epidemiology And Individualized Medicine Pharmacogenomics



Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting Biorxiv




Identification Of Genetics Molecular Biology Journals Facebook



Microrna Seed Region Length Impact On Target Messenger Rna Expression And Survival In Colorectal Cancer




Mirna Introduction Biogenesis Nomenclature And Experimental Workflow




Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Abstract Europe Pmc




Miraw A Deep Learning Approach To Predict Mirna Targets By Analyzing Whole Mirna Transcripts Biorxiv




Mismatches In The Mirna Proximal Seed Region Disrupt The Binding Download Scientific Diagram



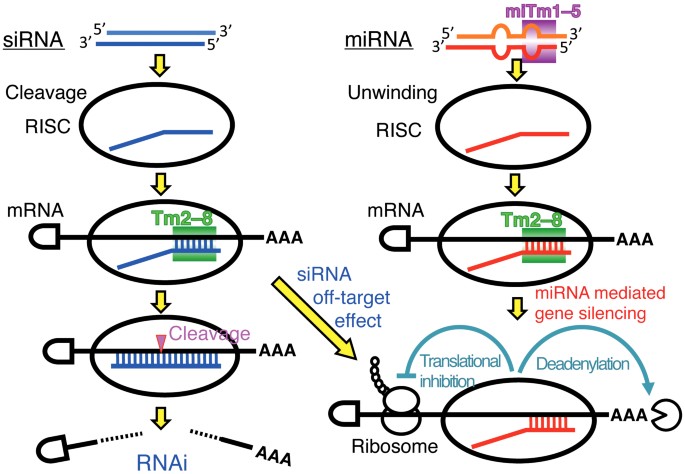
The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects



Targetscan Non Canonical Sites



Stability Of Mirna 5 Terminal And Seed Regions Is Correlated With Experimentally Observed Mirna Mediated Silencing Efficacy Scientific Reports




Cancers Free Full Text Detecting And Characterizing A To I Microrna Editing In Cancer Html



Stability Of Mirna 5 Terminal And Seed Regions Is Correlated With Experimentally Observed Mirna Mediated Silencing Efficacy Scientific Reports




Small Rna Seq Reveals Novel Mirnas Shaping The Transcriptomic Identity Of Rat Brain Structures Life Science Alliance




Microrna Wikipedia



1
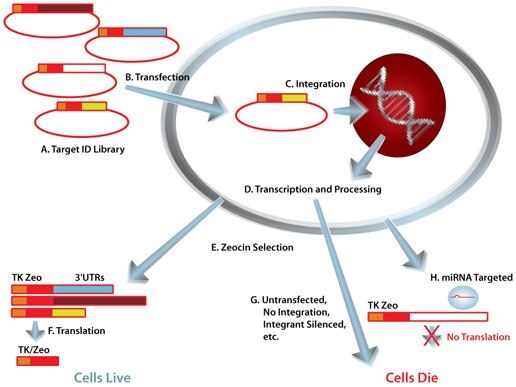



Mission Target Id Library For Human Mirna Target Id And Discovery




Function Control Of Anti Microrna Oligonucleotides Using Interstrand Cross Linked Duplexes Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
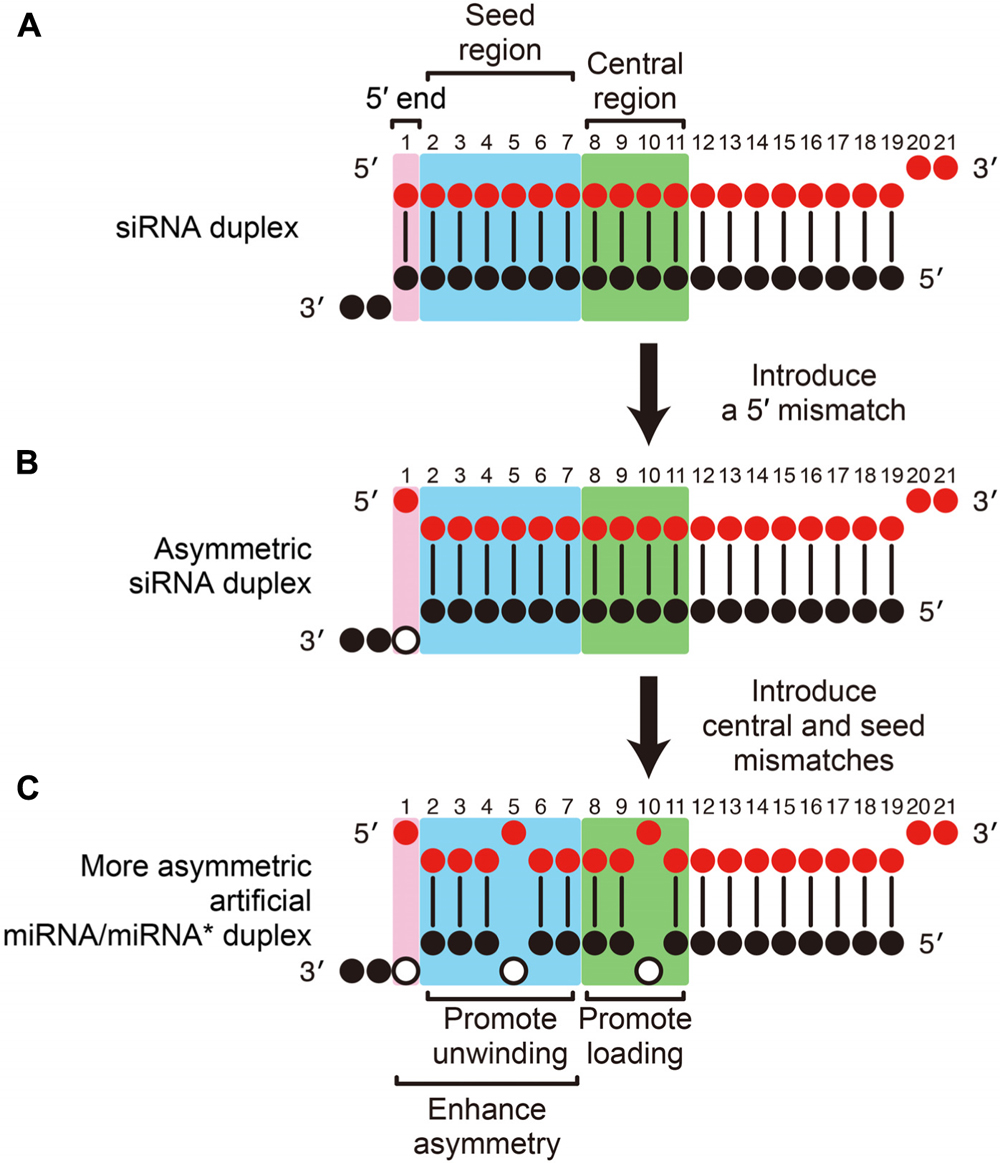



Frontiers Mirna Like Duplexes As Rnai Triggers With Improved Specificity Genetics




Mirna Targeting Growing Beyond The Seed Trends In Genetics




Miraw A Deep Learning Approach To Predict Mirna Targets By Analyzing Whole Mirna Transcripts Biorxiv



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿