Furthermore, since the introduction of polymiRTSs into seed regions can also affect miRNA mRNA binding efficiency, it can lead to either increased or decreased posttranscriptional mRNA regulation Finally, polymiRTSs may also affect miRNAbinding efficiency by changing supplemental seed pairing that applies to both canonical and noncanonical binding sitesKrek et al, 05) More than onethird About Cookies, including instructions on how to turn off cookies if you wish to do so By continuing to browse this site you agree to us using cookies as described in About Cookies Remove maintenance message

Prediction Of The Mirna Interactome Established Methods And Upcoming Perspectives Sciencedirect
Seed region of mirna
Seed region of mirna-Conserved WatsonCrick pairing to the 50 region of the miRNA, which includes the miRNA seed, enables prediction of targets above the background of falsepositive predictions, indicating the importance of this region for miRNA target recognition (Lewis et al, 03, 05;The seed sequence is essential for the binding of the miRNA to the mRNA The seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed sequence" has to be perfectly complementary




Microrna Wikipedia
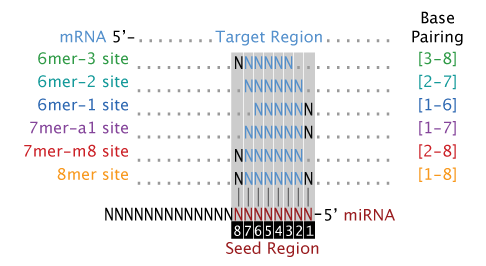
Of miRNA seed region polymorphisms (miRseedSNPs) consisting of 149 SNPs in six species Although a majority of detected polymorphisms were due to point mutations, two consecutive nucleotide substitutions (double nucleotide polymorphisms, DNPs) were also identified in nine miRNAs We determined that miRSNPs are frequently located within the quantitative trait loci Seed Pairing Is Enriched in miRNATarget Sites The miRNA sequence can be separated into five functional domains that affect miRNAtarget recognition 5′ anchor (nt 1), seed sequence (nts 2–8), central region (nts 9–12), 3′ supplementary region (nts 13–16), and 3′ tail (nts 17–22) (Wee et al, 12)Seed region of miRNA (nucleotides 2–8 at the 5'end), (2) "central gate" which matches the region from 9th to 13th nt of miRNA, and (3) "supplementary chamber" that comprises 3'end of the Molecules , 25, 2459 2 of 23 molecule Depending on the degree of complementarity between mRNA and miRNA the following scenarios of RNA processing might be realized 1) steric block of
Seed region of miRNA associated with Argonaute2 protein The seed region of the miRNA strand is shown Nucleotides 2 through 5 can be seen in positions that are able to interact with the complementary mRNA strand Nucleotides 1, 6 and 7 are notIf two miRNAs differ in their seed sequence for one nucleotide in theAtoI editing in the miRNA seed region regulates target mRNA selection and silencing efficiency Kume H(1), Hino K(2), Galipon J(2), UiTei K(3) Author information (1)Department of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, 731 Hongo, Bunkyoku, Tokyo , Japan Faculty of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, 731 Hongo, Bunkyoku, Tokyo
Page topic "Online GESS prediction of miRNAlike offtarget effects in largescale RNAi screen data by seed region analysis" Created by Floyd Little Language englishMicroRNA editing in seed region aligns with cellular changes in hypoxic conditions RNA editing is a finely tuned, dynamic mechanism for posttranscriptional gene regulation that has been thoroughly investigated in the last decadeChemical Modifications in the seed region of miRNAs 221/222 increase the silencing performances in gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells,




Sites Matching In The Mirna Seed Region Including All K Mer 8mer Download Scientific Diagram




Microrna Wikipedia
Is the miRNA seed region always located between the 2 and the 7 nucleotides?The latest version of this resource was released in August 15 miRSearchThe human genome encodes over 1000 miRNA genes that collectively target the vast majority of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) Basepairing of the socalled miRNA "seed" region with mRNAs identifies many thousands of putative targets Evaluating the strength of the resulting mRNA repression remains challenging, but is essential for a biologically informative ranking of potential miRNA



Http Genesdev Cshlp Org Content 19 9 1067 Full Pdf




Crispr Screening Strategies For Microrna Target Identification Yang The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library
6月 17, 21 Seed coat so that water and oxygen can enter the seeds In nature, hard seed coats are cracked or softened by fire, extreme temperatures, digestive acids in the stomachs of animals, or by the abrasion of blowing sand After the seed coat has beenMiRNA or miRNA duplexes with an overall higher BPP, with ADAR2 preferring targets with a high BPP in the root region Consistentwith priorstudies26,theseedregionsresponsiblefor target mRNA recognition were significantly more edited than nonseed regions for both ADARs Sequence motif alignments further revealed a difference in the breadth ofMost miRNA targets were of noncanonical type, ie without involving perfect pairing to canonical miRNA seed region Different miRNAs have distinct targeting patterns, and this miRNAtomiRNA variability was associated with seed sequence composition



Mirvestigator Framework Detect The Mirnas Driving Co Expression Signatures
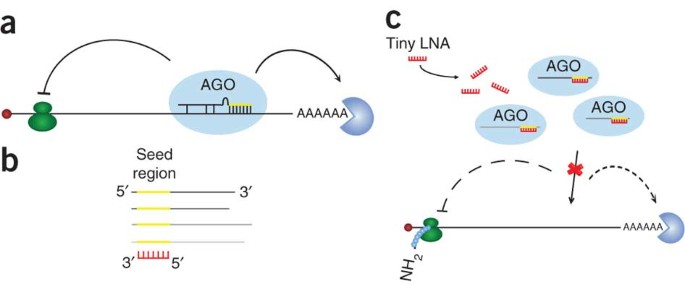



Silencing Of Microrna Families By Seed Targeting Tiny Lnas Nature Genetics
An overview of the seedplussupplementarypaired structure reveals the miRNA and target RNA form two discontinuous duplexes one composed of the seed region, and a secondary duplex in the supplementary region (Fig 1C and D) Within the seed region, the target RNA pairs to nucleotides g2–g8, with the t1adenosine sequestered within the t1binding pocket, as reported in seedTemperatures imply body temperatures for chickens (gga), humans (hsa), mice (mma), dogs (cfa), horses (eca), orangutans (ppy), and pigs (ssc), and rearing temperatures for "Stability of miRNA 5′terminal and seed regions is correlated with experimentally observed miRNA In the LNCaP exosomes, the 28 most highly expressed miRNAs had complementary seed regions, which were enriched in the exosomal lncRNAs Our analysis identified 18 motifs with U rich sequences and




Rna Targeting Utilizing Pairing Outside Of The Canonical Mirna 5 Seed Download Scientific Diagram




A Cartoon Showing The Site And Mechanism Of Mirna Targeting To Mrna Download Scientific Diagram
The seed regions are regions present within the miRNA binding regions Although there are several factors that pave a way to the binding between miRNA and mRNA, the impact of binding is determined by the seed sequence within the miRNA The seed region consists of a continuous string of at least 6 to 8 nucleotides miRNA recognizes its target byKim, Heo and Kim, 10;In miRNA targeting, the seed region (nt g2g7 or g2g8, from the miRNA 5' end) is the primary determinant for targeting efficacy and specificity, with over 80% of miRNAtarget under aCCBYND 40 International license not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity It is made available bioRxiv preprint doi The most conserved part of miRNA is located at 5′end and is called the seed region Guide (g) nucleotides from the seed region (g2–g7 or g2–g8) play a primary role in target recognition because more than 80% of the interactions between miRNAs and targets occurs via seed




Types Of Microrna Target Sites A There Are Three Types Of Canonical Download Scientific Diagram




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal
For the 1226 human miRNAs with SNPs in their seed region, 314 (256%) of them are located in miRNA clusters, whereas among the 1587 human miRNAs without SNPs in their seed region, only 3 (2%) of them are located in miRNA clusters (P = 606 x 10sup4, chi square test) (Table S2) miRNAs from the same cluster have the tendency to regulate the sameBrennecke et al, 05;Tered miRNA seed regions with that of SNPs in nonclustered miRNA seed regions We found that the percent overlap of SNPs in clustered miRNA seed regions is much higher than that of SNPs in nonclustered miRNA seed regions (Student's ttest;




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal



1
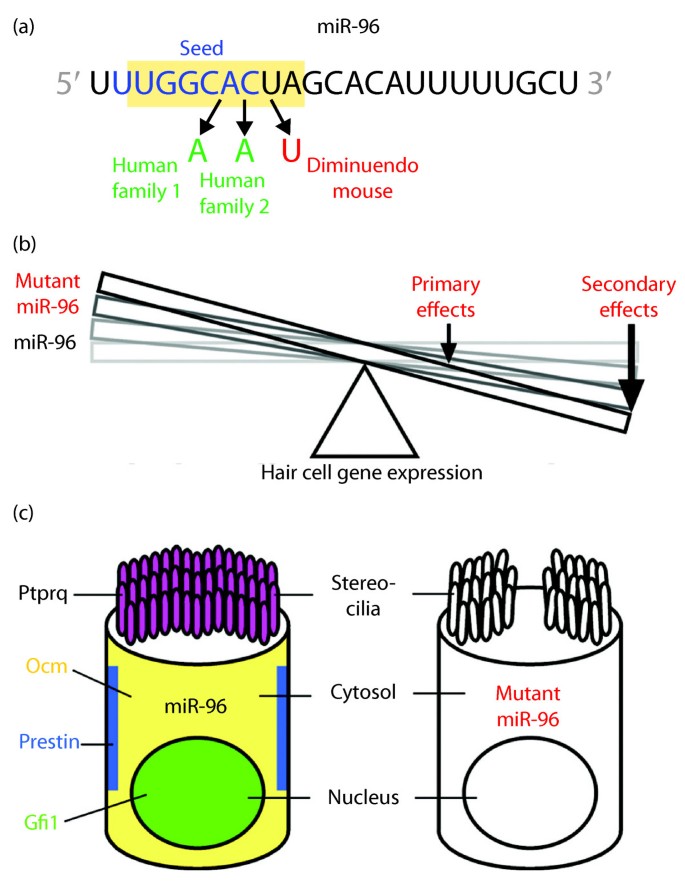
However, no pathogenic mutations within the mature sequence of a miRNA have been reported so far Here we show that point mutations in the seed region of miR96, a miRNA expressed in hair cells of Although littletono basepairing is usually observed between siRNA nonseed region (nucleotides 9– in Fig 1C) and the corresponding offtarget region, it was previously reported with miRNAs that such partial basepairing is an additional factor that influences the efficiency of seeddependent knockdown 18 , and was thus included in our analysisExosomal lncRNAs are themselves enriched for miRNA seeds with a preference for let7 family members as well as miR17, miR18a, miRa, miR93 and miR106b The enrichment of miRNA seed regions




Microrna Polymorphisms The Future Of Pharmacogenomics Molecular Epidemiology And Individualized Medicine Pharmacogenomics



Micrornas Sound Off Genome Medicine Full Text
For the 1226 human miRNAs with SNPs in their seed region, 314 (256%) of them are located in miRNA clusters, whereas among the 1587 human miRNAs without SNPs in their seed region, only 3 (2%) of them are located in miRNA clusters (P = 606 × 10 −4, χ 2 test) (Table S2) miRNAs from the same cluster have the tendency to regulate the same sets of target genesOnline GESS prediction of miRNAlike offtarget effects in largescale RNAi screen data by seed region analysis Bahar Yilmazel1, Yanhui Hu1, Frederic Sigoillot2, Jennifer A Smith3, Caroline E Shamu3, Norbert Perrimon1,4 and Stephanie E Mohr1* Abstract Background RNA interference (RNAi) is an effective and important tool used to study gene function For largescale screens, This region is known as "seedregion" and found at the 27 base of the miRNA This region is able to suppress the target mRNAs without having a complete base pairing at the 3'end of the miRNA Another class involves the improper complementary base pairing at the 5'end of the miRNAs, but to overcome this imperfect pairing, there are some additional base pairings at the 3'



Www Cell Com Cell Pdf S0092 8674 18 1 Pdf




Microrna Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms And Diabetes Mellitus A Comprehensive Review Zhang 19 Clinical Genetics Wiley Online Library
TargetScan is a target prediciton tool that predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of conserved 8mer and 7mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA The target prediction software is frequently updated;Pasquinelli, 12) In contrast, most evidence indicates that miRNAs in land plants require more extensive pairing to their targets (Schwab et al, 05; The nucleotides 28 in miRNA are termed 'seed,' which is the most crucial region for target recognition The seed region undergoes WatsonCrick base pairing with 3'UTR of mRNAs The degree of mRNA destabilization differs according to the class of the target site The different classes(of target sites to seed) are given below with increasing efficacy and preferential



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Miraw A Deep Learning Approach To Predict Mirna Targets By Analyzing Whole Mirna Transcripts Biorxiv
Seed region Seed region of mirna リンクを取得 ; It is thought that most miRNAmRNA interactions involve the seed region at the 5′ end of the miRNA The importance of seed sites is supported by experimental evidence, although there is growing interest in interactions mediated by the central region ofVealed that target hybridization to nucleotides of the seed region, at the 5′ end of an miRNA, was sufficient to induce moderate repression of expression In contrast, pairing to the 3′ region of the miRNA was not critical for silencing Our results suggest that the basepairing requirements for small RNAmediated repression in C reinhardtii are more similar to those of metazoans




Mirbase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Microrna Wikipedia
Canonically, miRNA targeting is reliant on base pairing of the seed region, nucleotides 2–7, of the miRNA to sites in mRNA 3′ untranslated regions Recently, the 3′ half of the miRNA has gained attention for newly appreciated roles in regulating target specificity and regulation In addition, the extent of pairing to the miRNA 3′ end In the present study, examination was made of RNA requirements in the nonseed region of siRNA The nonseed region of siRNA was found to be subdivided into four domains, in which two nucleotide pairs (positions 13 and 14) were replaceable with cognate deoxyribonucleotides without reducing RNAi activityAtoI editing in the miRNA seed region regulates target mRNA selection and silencing efficiency 11 Pages AtoI editing in the miRNA seed region regulates target mRNA selection and silencing efficiency Nucleic acids research, 14 Josephine Galipon Download PDF Download Full PDF Package This paper A short summary of this paper 37 Full PDFs related to this paper READ



Plos One Evolution Of Microrna In Primates




Systematic Prediction Of The Impacts Of Mutations In Microrna Seed Sequences
A mismatch tolerance test assay, based on pools of transgenic strains, revealed that target hybridization to nucleotides of the seed region, at the 5′ end of an miRNA, was sufficient to induce moderate repression of expression In contrast, pairing to the 3′ region of the miRNA was not critical for silencing Furthermore, we evaluated the silencing efficiencies of miRNAs with the Base pairing of the miRNA seed region (positions 2–8 from the 5′ end of an miRNA) in animals is critical for target recognition and repression (Bartel, 09; The nucleotides 2–8 of the 5′ region of the miRNA, known as the "seed site" decides the specific target recognition The short seed region necessary for miRISC function determines that a single miRNA may target multiple mRNAs



Upcommons Upc Edu Bitstream Handle 2117 Pdf Sequence 1 Isallowed Y




Example Of Mirna Target Alignment This Schematic Representation Shows Download Scientific Diagram
The SNP identified in our study is located in the seed region of the miRNA that has to be complementary to the mRNA in order to recognize the target MiRSNP could impact on the catalogue of miRNA targets, not only by disrupting the interaction of the mutant Mir717 with some target genes but also by creating illegitimate targets that are not targeted by the wild typeMiRNA function is evidenced by the fact that the seed region sequence of many miRNA families is highly conserved both within and between species 9 Mature singlestranded miRNAs bound to the RNAinduced silencing complex (RISC) recognize their regulatory targets by WatsonCrick base pairing to compatible sequences (usually in 39 untranslated regions or 39 UTRs) in target
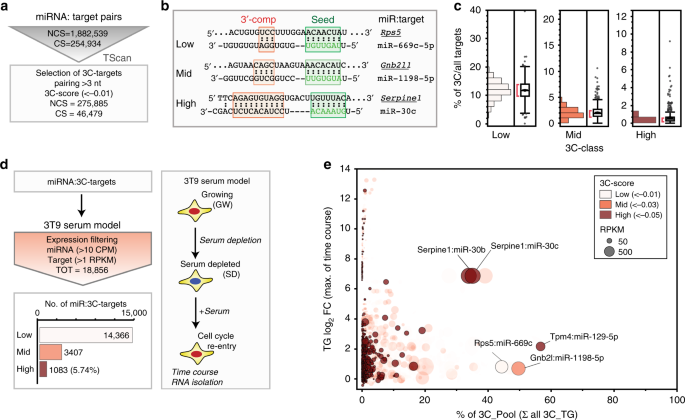



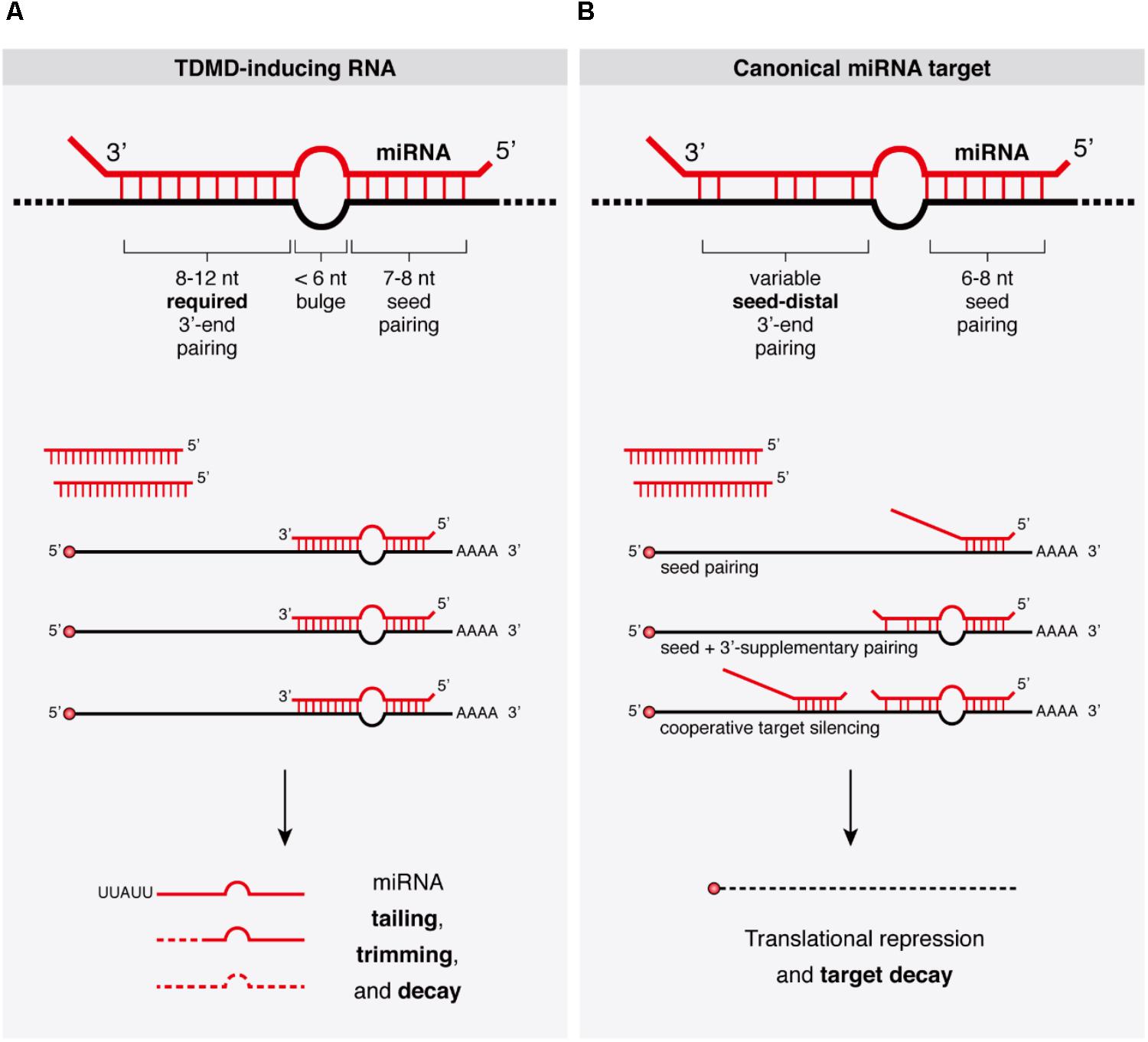
Endogenous Transcripts Control Mirna Levels And Activity In Mammalian Cells By Target Directed Mirna Degradation Nature Communications
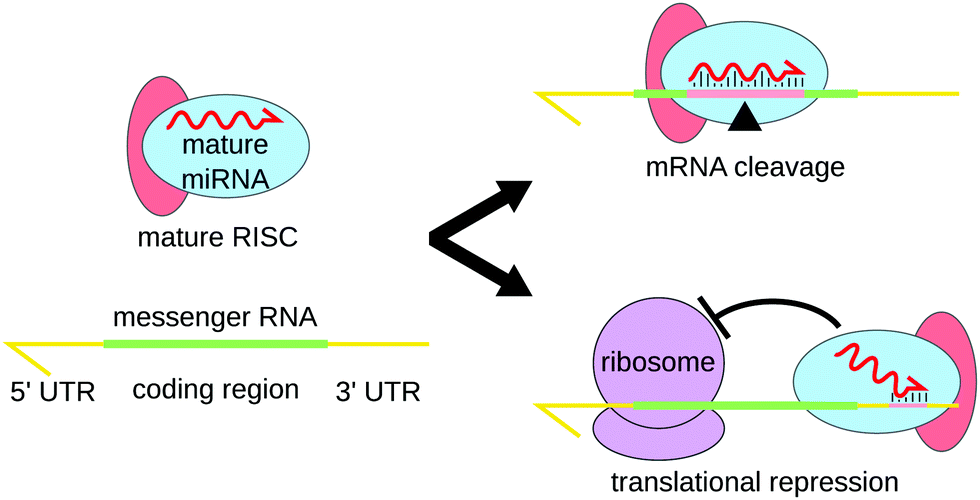



Advances In Multiplexed Techniques For The Detection And Quantification Of Micrornas Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0csb
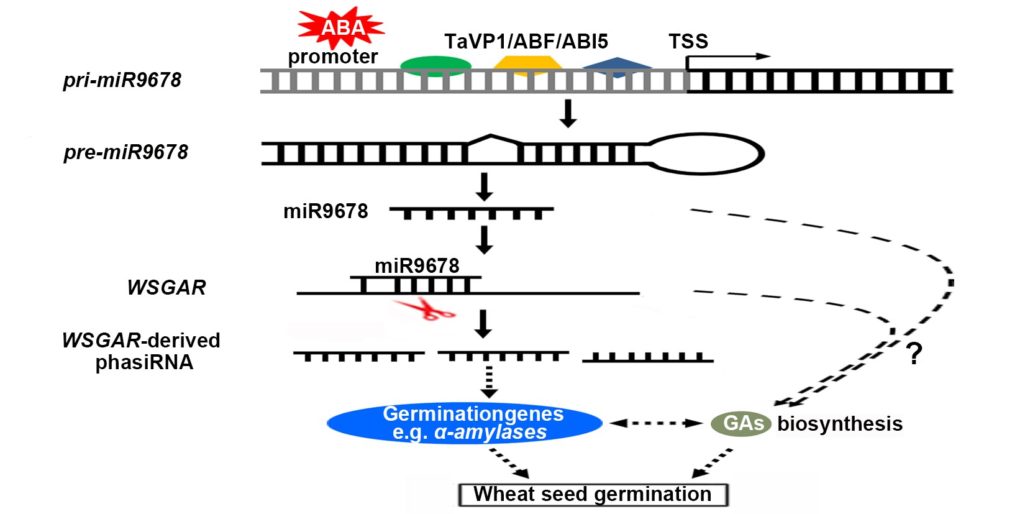



Plantae Mirna Mediated Regulation Of Germination Plantae




A Study Of Micrornas In Silico And In Vivo Bioimaging Of Microrna Biogenesis And Regulation Kim 09 The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library
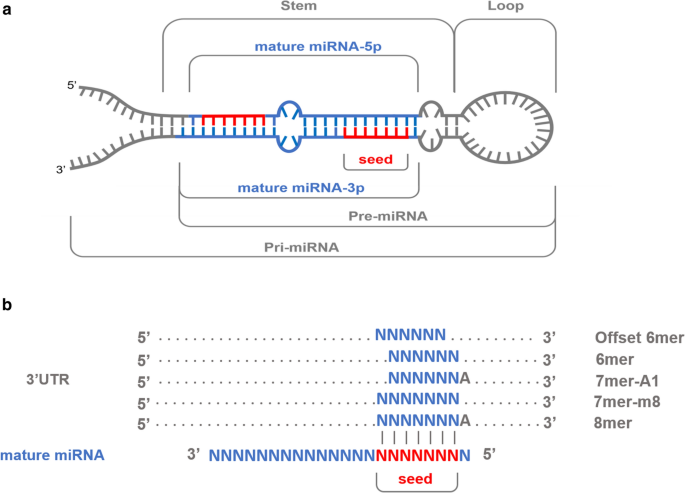



Variability In Porcine Microrna Genes And Its Association With Mrna Expression And Lipid Phenotypes Genetics Selection Evolution Full Text



Www Longdom Org Open Access Micrornas In Skin Biology Biogenesis Regulations And Functions In Homeostasis And Diseases Pdf




Snps In Microrna Target Sites And Their Potential Role In Human Disease Open Biology




Dbmts A Comprehensive Database Of Putative Human Microrna Target Site Snvs And Their Functional Predictions Li Human Mutation Wiley Online Library




A Simplified System To Express Circularized Inhibitors Of Mirna For Stable And Potent Suppression Of Mirna Functions Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
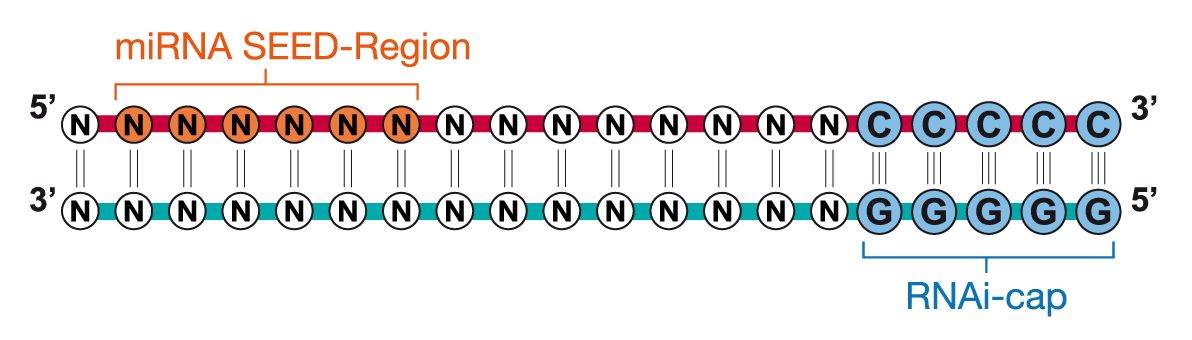



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna



Cells Free Full Text The Butterfly Effect Of Rna Alterations On Transcriptomic Equilibrium Html




Mirna Sequencing Report




Mirna Introduction Biogenesis Nomenclature And Experimental Workflow




Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Cell



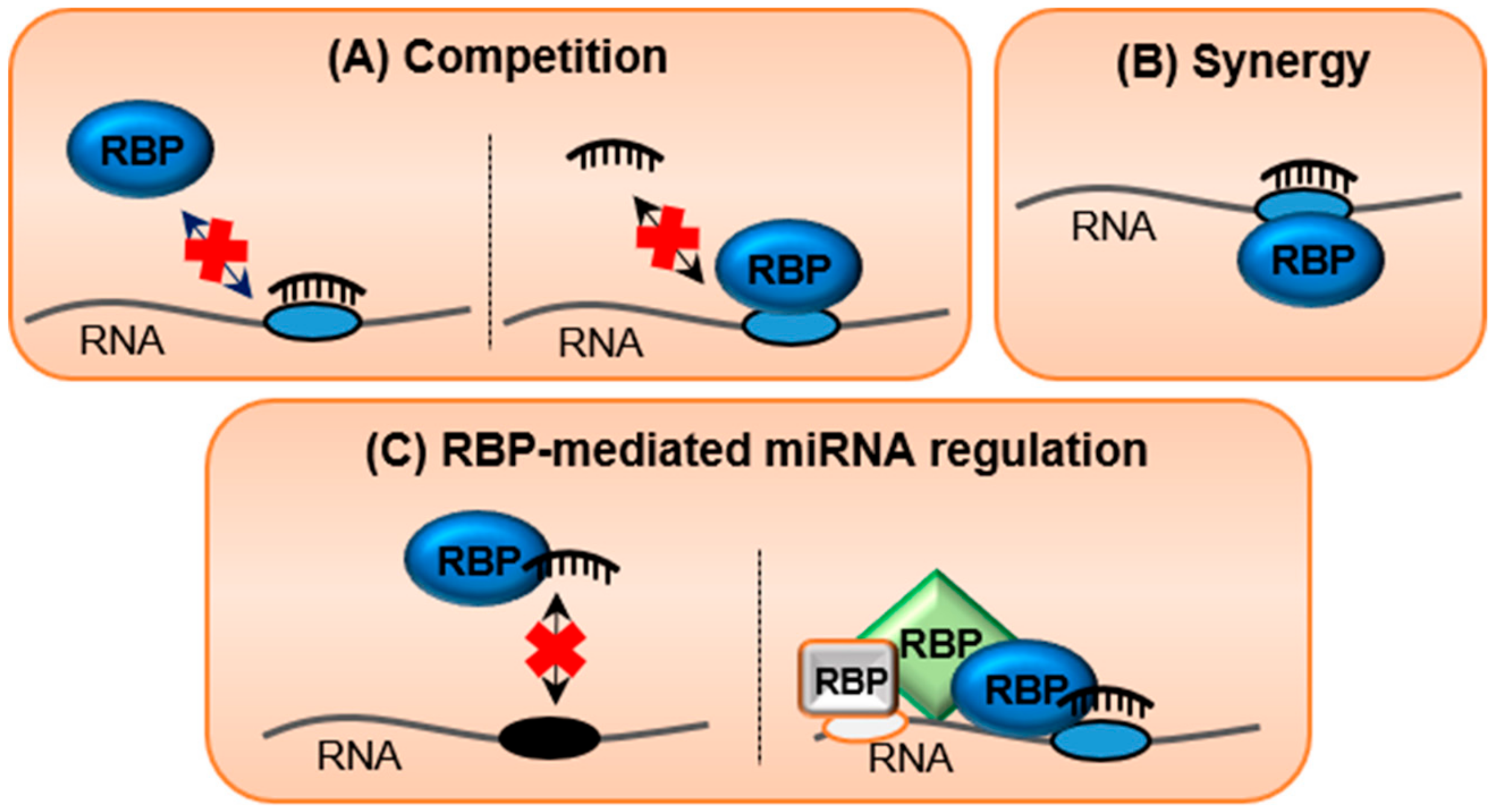
Frontiers Target Rnas Strike Back On Micrornas Genetics




Mirna Sequencing Report



1
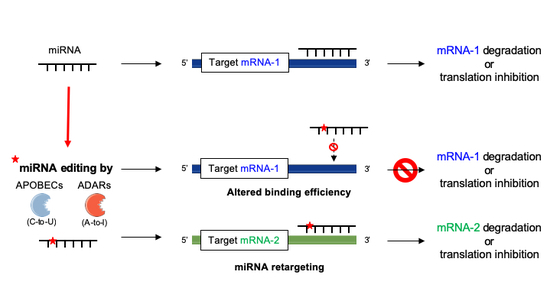



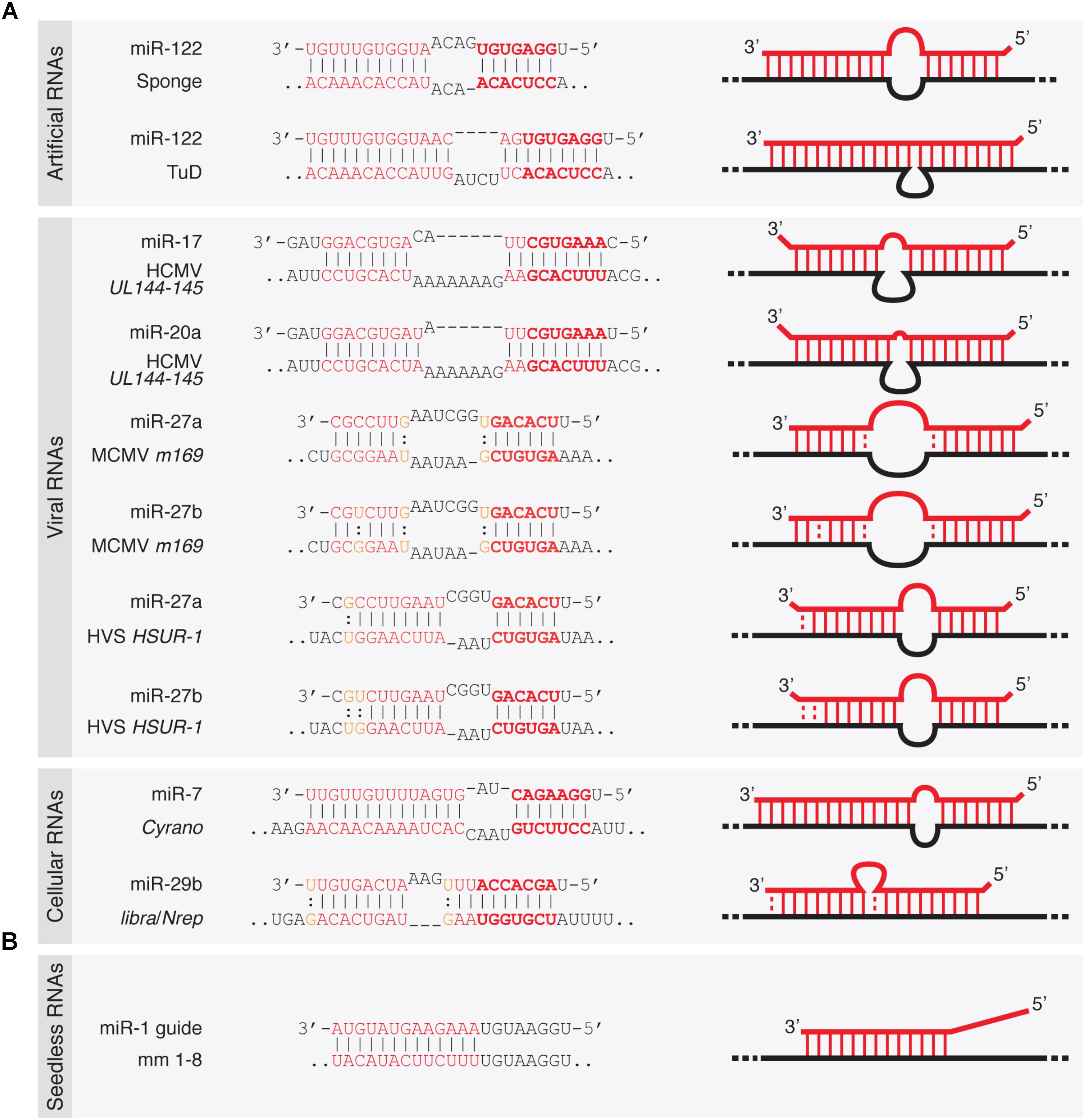
Ijms Free Full Text Deciphering Mirnas Action Through Mirna Editing Html



Frontiers Target Rnas Strike Back On Micrornas Genetics
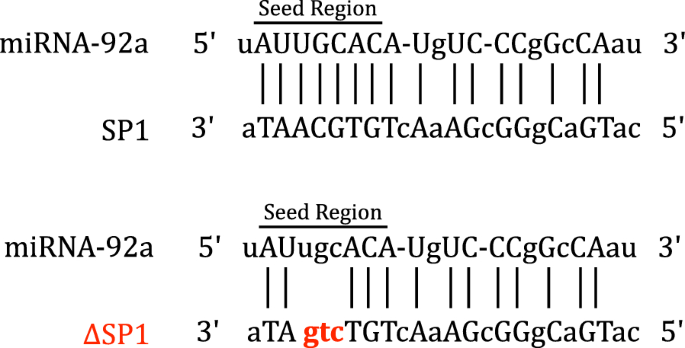



Microrna 92a Regulates The Expression Of Aphid Bacteriocyte Specific Secreted Protein 1 Bmc Research Notes Full Text
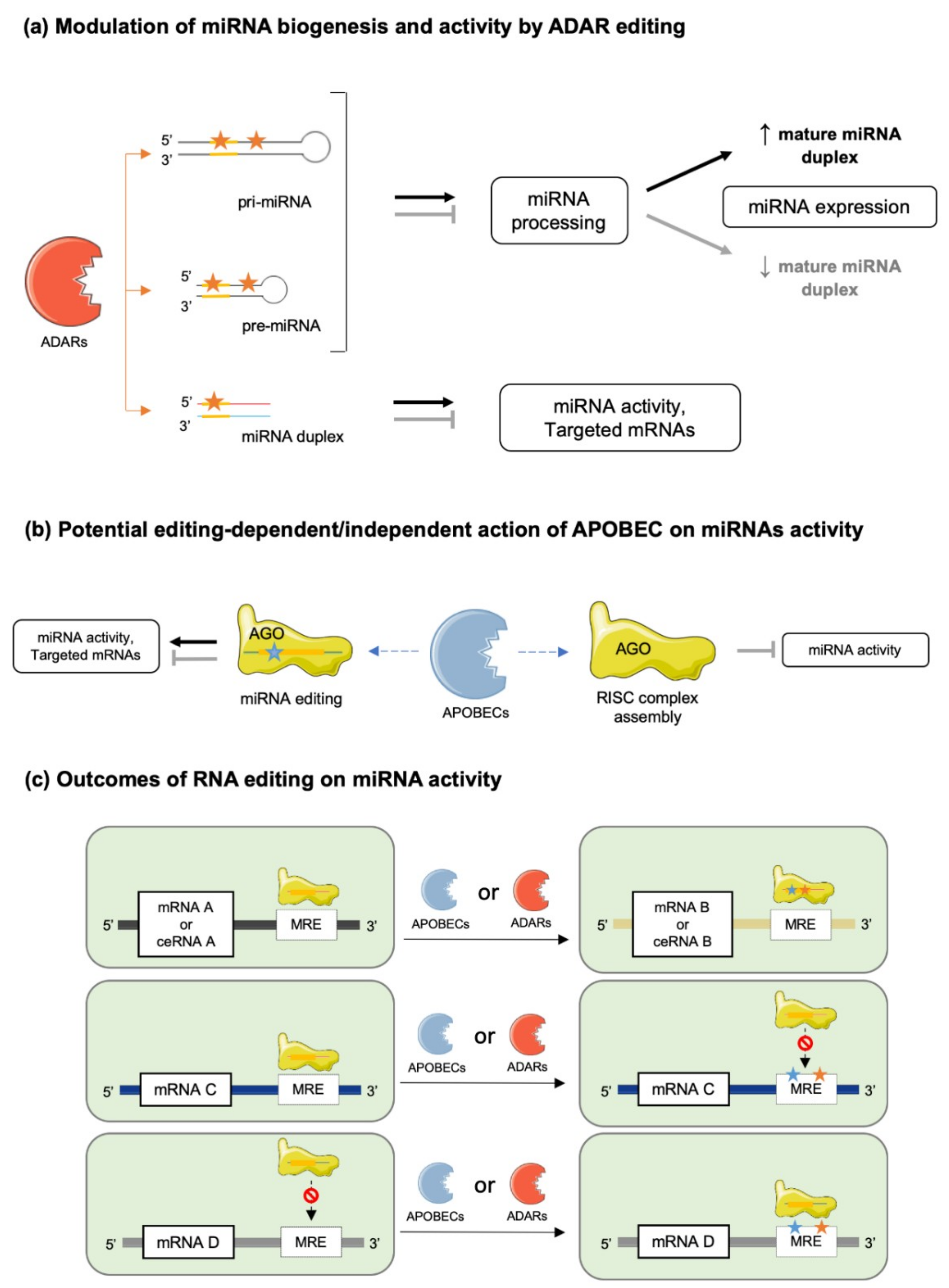



Ijms Free Full Text Deciphering Mirnas Action Through Mirna Editing Html




Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids




Rna Mrna Target Interaction Schematic Overview Of A Mirna Interaction Download Scientific Diagram




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science



Plos One Micrornas Mir 19 Mir 340 Mir 374 And Mir 542 Regulate Mid1 Protein Expression



Microrna Seed Region Length Impact On Target Messenger Rna Expression And Survival In Colorectal Cancer
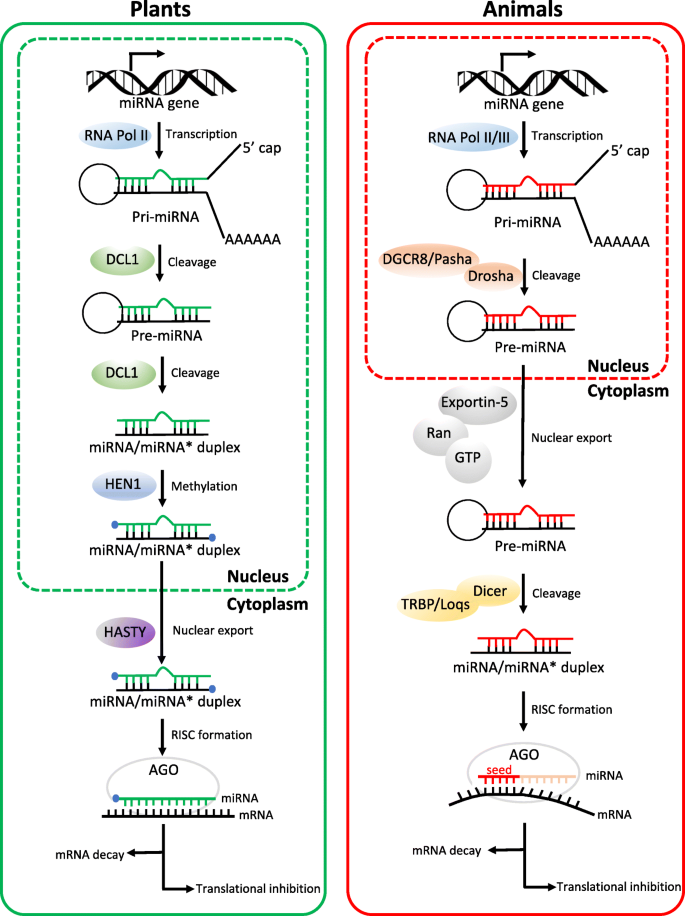



Micrornas From Plants To Animals Do They Define A New Messenger For Communication Nutrition Metabolism Full Text



Targetscan Non Canonical Sites
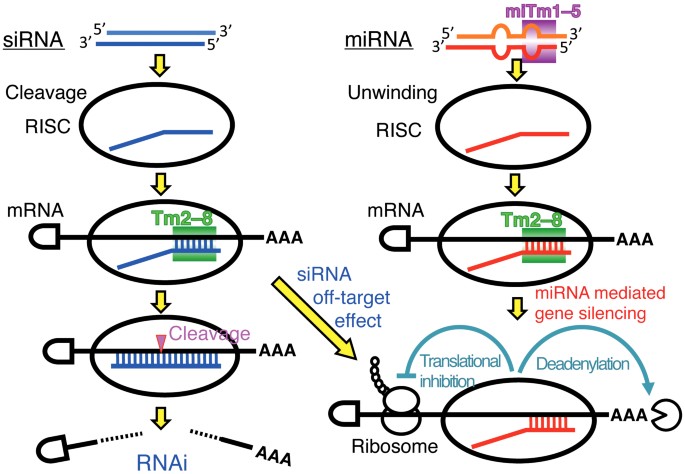



Stability Of Mirna 5 Terminal And Seed Regions Is Correlated With Experimentally Observed Mirna Mediated Silencing Efficacy Scientific Reports




Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Cell



Microrna Mediated Target Mrna Cleavage And 3 Uridylation In Human Cells Scientific Reports




Rational Design Of Highly Efficient Artificial Mirna Mirna Download Scientific Diagram




Snps In Microrna Target Sites And Their Potential Role In Human Disease Open Biology



Plos One Identification And Characteristics Of Micrornas From Army Worm Spodoptera Frugiperda Cell Line Sf21




Mirna Seed Regions Are Defined By Structural Backbone Rigidity A Download Scientific Diagram




Microrna Regulation And Cardiac Calcium Signaling Circulation Research
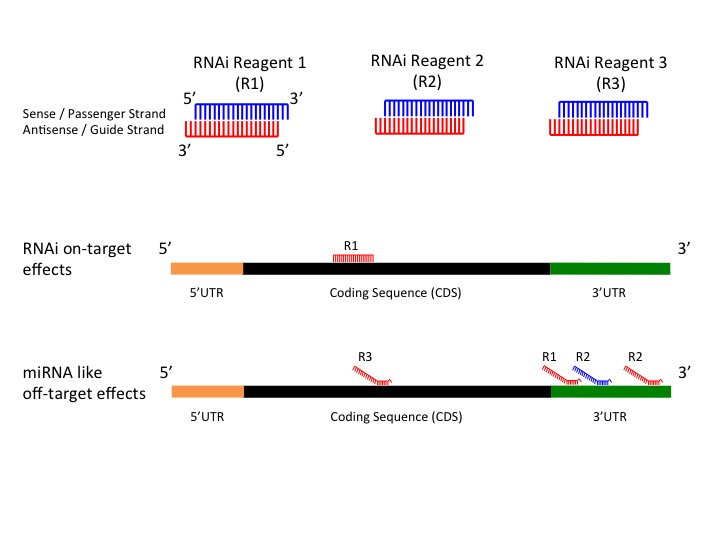



Gess




Pairing Beyond The Seed Supports Microrna Targeting Specificity Sciencedirect




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science
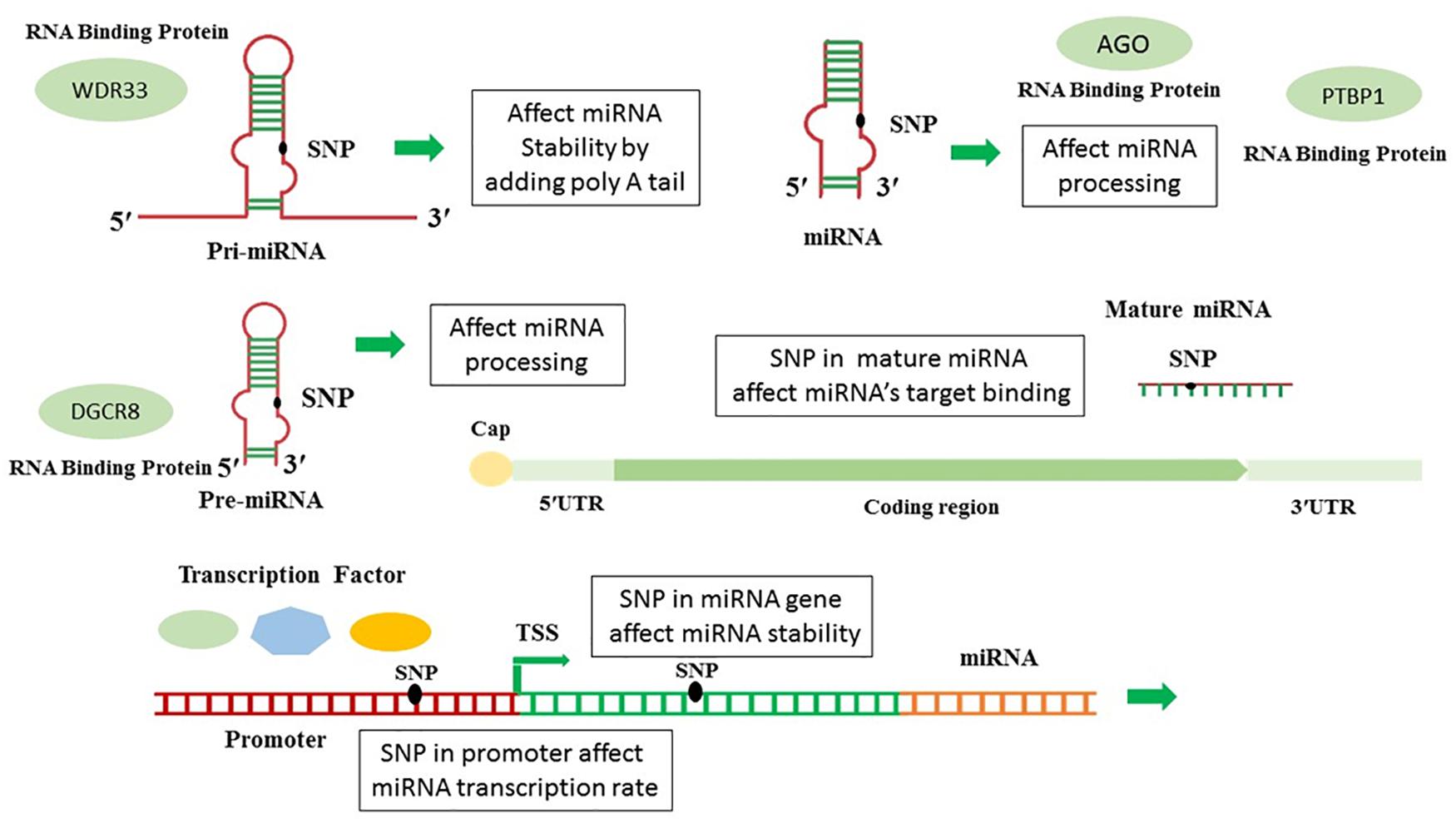



Frontiers In Silico Analysis Of Polymorphisms In Micrornas Deregulated In Alzheimer Disease Neuroscience




Mirna Introduction Biogenesis Nomenclature And Experimental Workflow




Different Seed Match Regions Of Mirnas Mirnalyze Follows A Download Scientific Diagram




Human Polymorphism At Micrornas And Microrna Target Sites Pnas




Ndownloader Figstatic Com Files Preview




Examples Of Mirna Target Interactions Pairing Schemes Of Several Download Scientific Diagram




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science




Types Of Mirna Target Sites And Multiple Sites A Stringent Seed Download Scientific Diagram




Mismatches In The Mirna Proximal Seed Region Disrupt The Binding Download Scientific Diagram




Mirna Targeting Growing Beyond The Seed Trends In Genetics
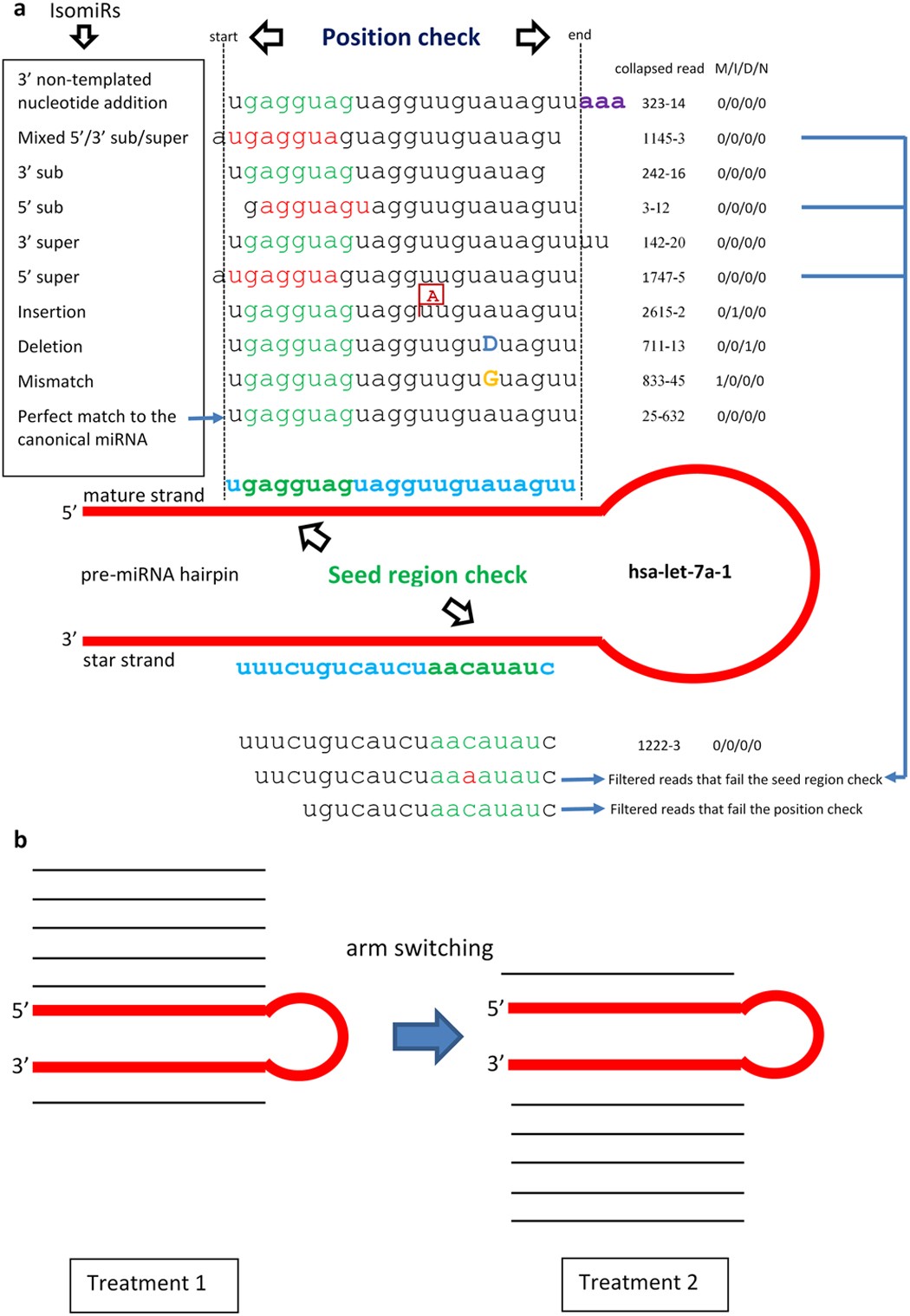



Mirpro A Novel Standalone Program For Differential Expression And Variation Analysis Of Mirnas Scientific Reports




3 Uridylation Confers Mirnas With Non Canonical Target Repertoires Sciencedirect
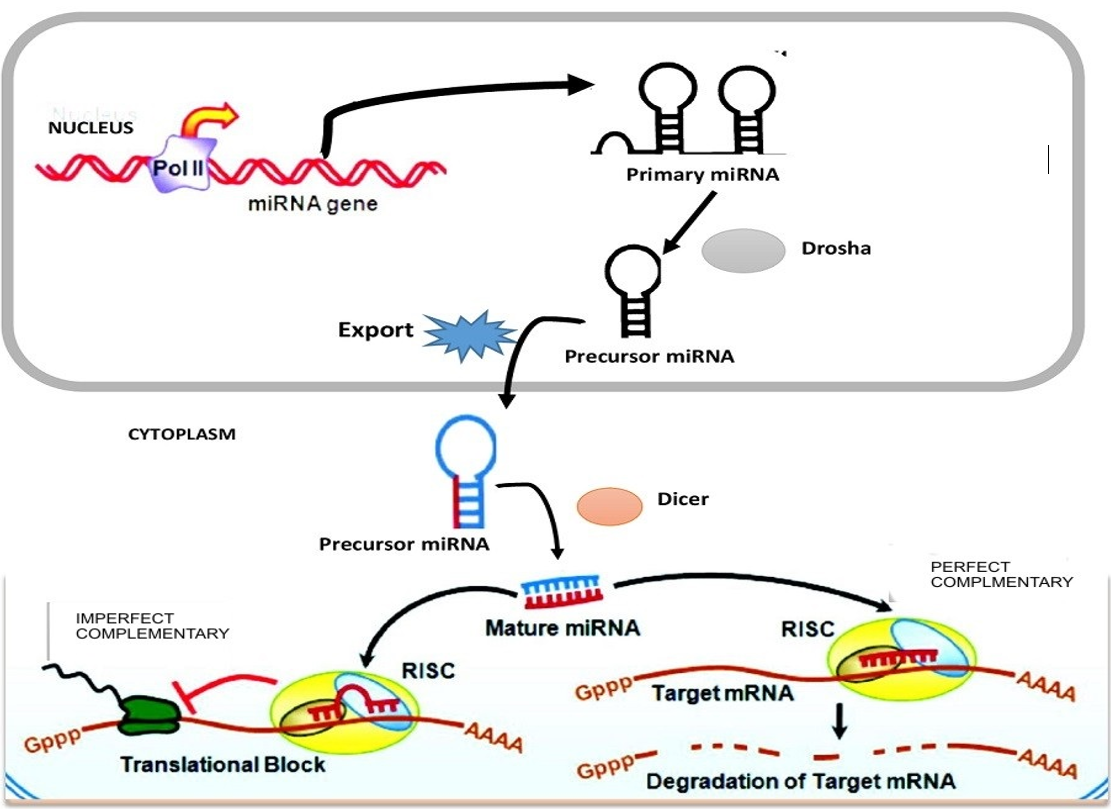



Pre Diagnostic Role Of Platelet Mirna In Coronary Heart Disease Of Healthy Overweight Subjects Via Platelet Leptin Receptor Activation Biomedical Research And Therapy




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal




Mirna Microrna Target Prediction Validation And Functional Abm Inc




Microrna Wikipedia




Mismatches In The Mirna Proximal Seed Region Disrupt The Binding Download Scientific Diagram




Chemical Modifications In The Seed Region Of Mirnas 221 222 Increase The Silencing Performances In Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Cells Sciencedirect




Structural Differences Between Pri Mirna Paralogs Promote Alternative Drosha Cleavage And Expand Target Repertoires Sciencedirect




Prediction Of The Mirna Interactome Established Methods And Upcoming Perspectives Sciencedirect



1
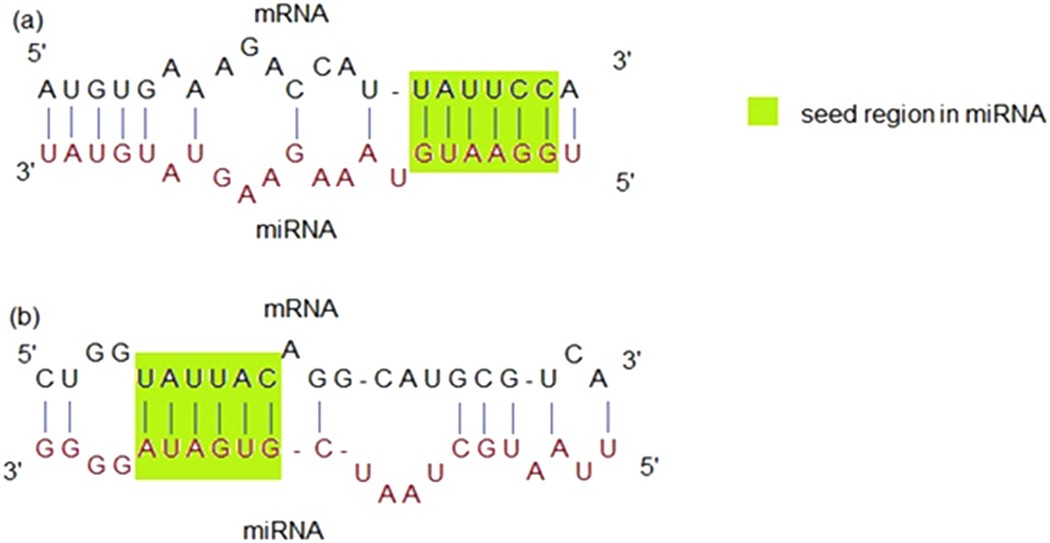



Mirepress Modelling Gene Expression Regulation By Microrna With Non Conventional Binding Sites Scientific Reports
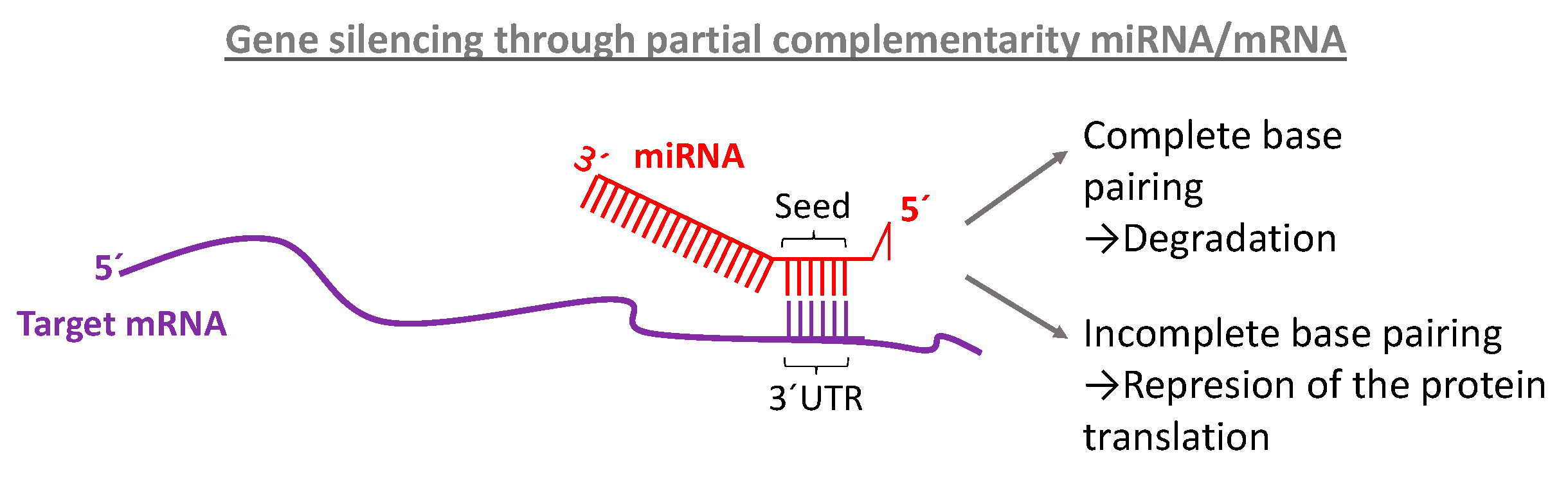



Ijms Free Full Text Microrna Nanotherapeutics For Lung Targeting Insights Into Pulmonary Hypertension Html




Mirpro A Novel Standalone Program For Differential Expression And Variation Analysis Of Mirnas Scientific Reports




Mirna Therapeutics A New Class Of Drugs With Potential Therapeutic Applications In The Heart Future Medicinal Chemistry




Pairing Beyond The Seed Supports Microrna Targeting Specificity Sciencedirect




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Biorxiv




Miraw A Deep Learning Approach To Predict Mirna Targets By Analyzing Whole Mirna Transcripts Biorxiv



Silo Tips Download How To Measure Mirna Expression Matt Barter




Extracellular Micrornas In Human Circulation Are Associated With Mirisc Complexes That Are Accessible To Anti Ago2 Antibody And Can Bind Target Mimic Oligonucleotides Pnas



1




Clustering Pattern And Functional Effect Of Snps In Human Mirna Seed Regions




Helix 7 In Argonaute2 Shapes The Microrna Seed Region For Rapid Target Recognition The Embo Journal




Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
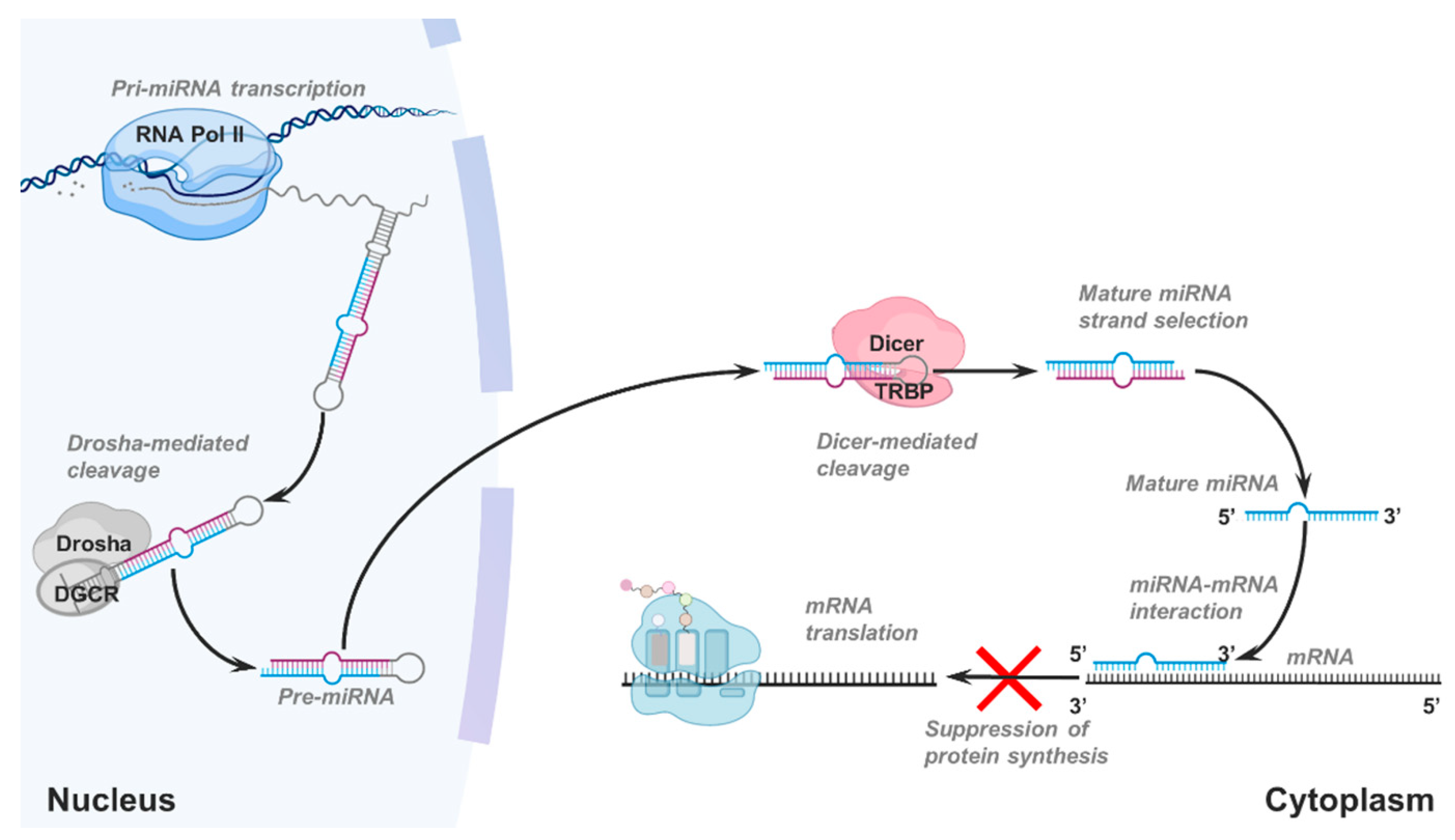



Cancers Free Full Text Detecting And Characterizing A To I Microrna Editing In Cancer Html
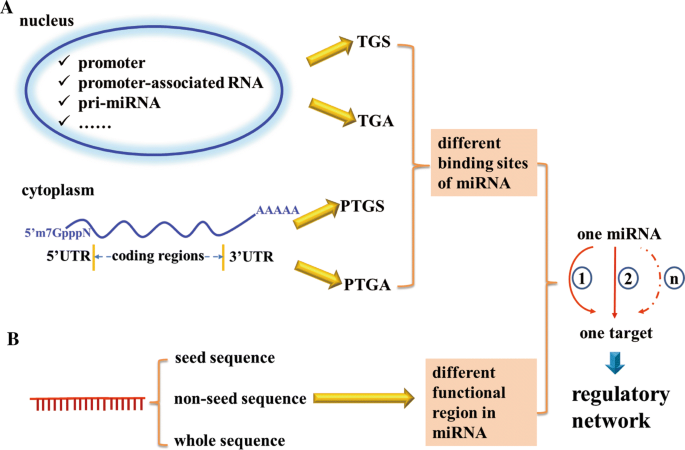



Regulatory Network Of Mirna On Its Target Coordination Between Transcriptional And Post Transcriptional Regulation Of Gene Expression Springerlink
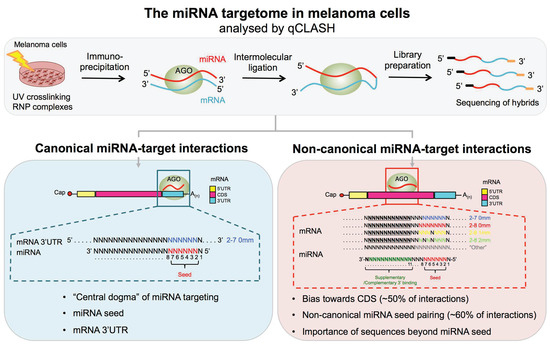



Cancers Free Full Text Cross Linking Ligation And Sequencing Of Hybrids Qclash Reveals An Unpredicted Mirna Targetome In Melanoma Cells Html




An Overview Of The Mirna Processing Pathway And Mechanism Of Mirna Download Scientific Diagram




Mirna Sequencing Report
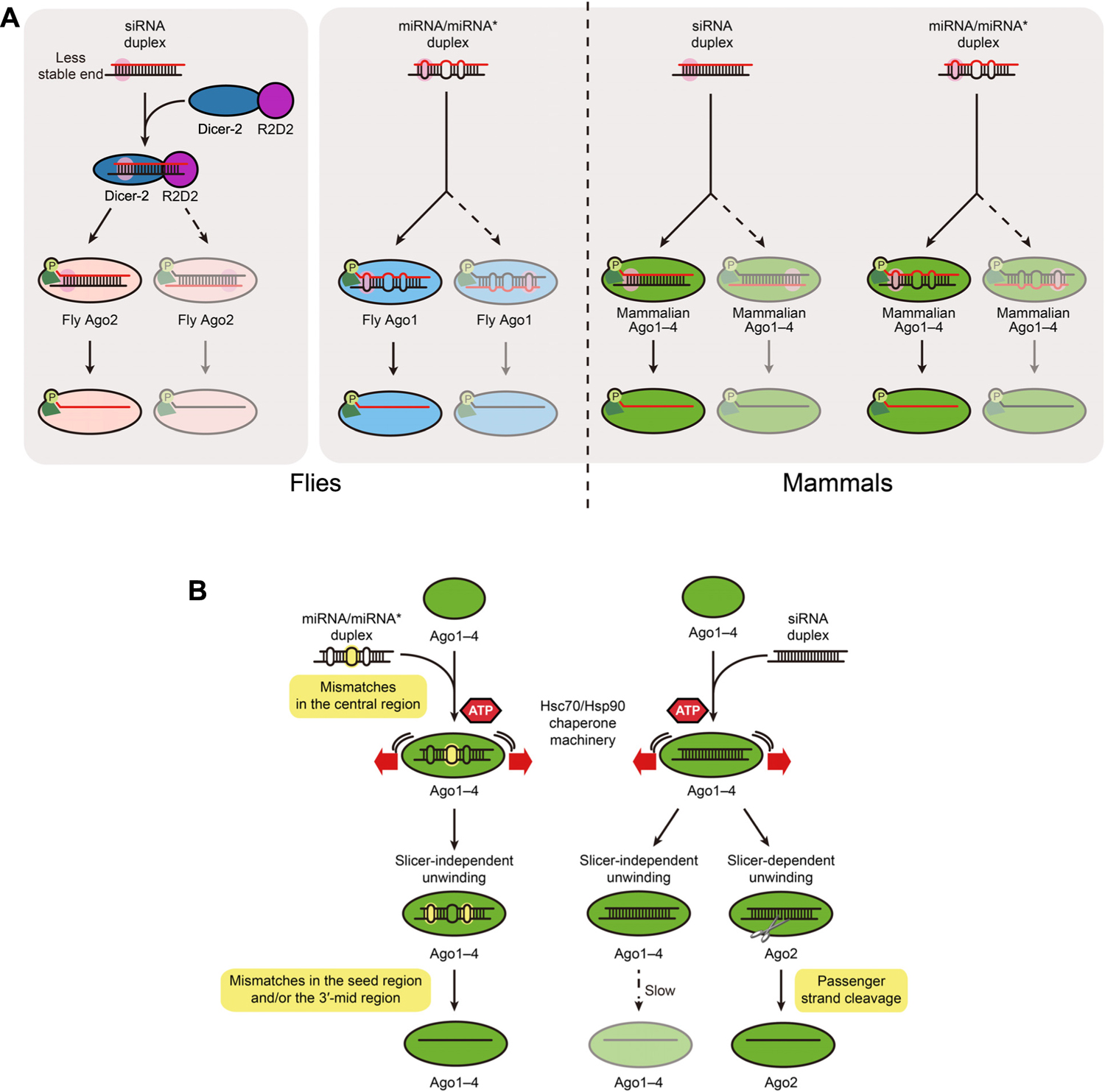



Frontiers Mirna Like Duplexes As Rnai Triggers With Improved Specificity Genetics




Dbmts A Comprehensive Database Of Putative Human Microrna Target Site Snvs And Their Functional Predictions Li Human Mutation Wiley Online Library



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿